Be part of prime executives in San Francisco on July 11-12, to listen to how leaders are integrating and optimizing AI investments for achievement. Be taught Extra
Patch administration approaches that aren’t data-driven are breaches ready to occur. Attackers are weaponizing years-old CVEs as a result of safety groups are ready till a breach occurs earlier than they prioritize patch administration.
Cyberattackers’ rising tradecraft now contains larger contextual intelligence about which CVEs are most weak. The end result: Handbook approaches to patch administration — or overloading endpoints with too many brokers — leaves assault surfaces unprotected, with exploitable reminiscence conflicts.
In the meantime, attackers proceed honing their tradecraft, weaponizing vulnerabilities with new methods and applied sciences that evade detection and may defeat handbook patch administration methods.
CrowdStrike’s 2023 World Menace Report discovered malware-free intrusion exercise accounts for as much as 71% of all detections listed by the CrowdStrike Menace Graph. Forty–seven % of breaches resulted from unpatched safety vulnerabilities. Over half of organizations, or 56%, remediate safety vulnerabilities manually.
Occasion
Remodel 2023
Be part of us in San Francisco on July 11-12, the place prime executives will share how they’ve built-in and optimized AI investments for achievement and averted widespread pitfalls.
Register Now
Should you want even additional proof that counting on handbook patching strategies doesn’t work, take into consideration this: 20% of endpoints after remediation are nonetheless not present on all patches, leaving them weak to breaches once more.
“Patching will not be almost so simple as it sounds,” mentioned Dr. Srinivas Mukkamala, chief product officer at Ivanti. “Even well-staffed, well-funded IT and safety groups expertise prioritization challenges amidst different urgent calls for. To cut back danger with out growing workload, organizations should implement a risk-based patch administration resolution and leverage automation to establish, prioritize and even handle vulnerabilities with out extra handbook intervention.”
Distributors fast-tracking risk-based vulnerability administration and AI
CISOs inform VentureBeat that legacy patch administration methods are a part of their tech stack consolidation plans due to risk-based vulnerability administration (RBVM), an strategy that gives larger efficacy and is faster to deploy as a result of it’s cloud-based. AI-based patch administration depends partially on algorithms that want a continuous stream of knowledge to be able to maintain “studying” and assessing patch vulnerabilities. Search for main distributors which are a number of product-generations into their AI and machine studying improvement to set the tempo of the market.
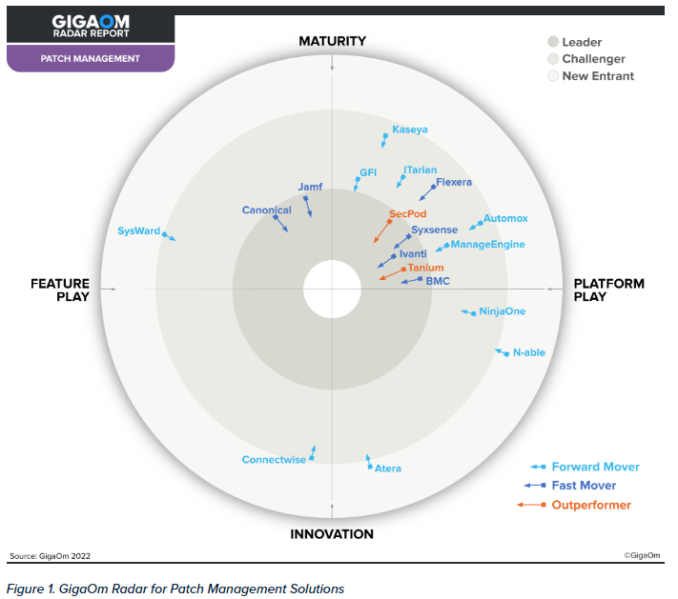
The GigaOm Radar for Patch Administration Options Report highlights the technical strengths and weaknesses of the highest patch administration suppliers. As a result of it compares distributors available in the market segments served by deployment fashions and patch protection and assesses every vendor, this a noteworthy report. The report analyzed distributors together with Atera, Automox, BMC Shopper Administration Patch powered by Ivanti, Canonical, ConnectWise, Flexera, GFI, ITarian, Ivanti, Jamf, Kaseya, ManageEngine, N-able, NinjaOne, SecPod, SysWard, Syxsense and Tanium.

Supply: GigaOm Radar for Patch Administration Options Report
It takes a breach to interrupt a reactive guidelines mentality
CISOs from main insurance coverage and monetary companies corporations inform VentureBeat anonymously that the urgency to patch endpoints and mission-critical methods sometimes begins solely when a system is breached resulting from down-rev patches on endpoints. It’s a reactive, not prescriptive reflex, as one CISO confided to VentureBeat not too long ago. Typically it takes a big occasion, whether or not an intrusion, a breach of a mission-critical system or the invention of stolen entry credentials, to escalate the mandatory patching work.
What CISOs are telling us is in keeping with Ivanti’s State of Safety Preparedness 2023 Report. Ivanti discovered that 61% of the time, an exterior occasion, intrusion try or breach reinitiates patch administration efforts. Although organizations are racing to defend in opposition to cyberattacks, the trade nonetheless has a reactive, guidelines mentality. Greater than 9 out of 10 safety professionals mentioned they prioritize patches, however in addition they mentioned every kind rank excessive, which means none does.

Picture supply: Ivanti’s State of Safety Preparedness 2023 Report
5 methods AI-driven patch administration is shaking up cybersecurity
Automating patch administration whereas capitalizing on various datasets and integrating it into an RBVM platform is an ideal use case of AI in cybersecurity. Main AI-based patch administration methods can interpret vulnerability evaluation telemetry and prioritize dangers by patch sort, system and endpoint. Danger-based scoring is why AI and machine studying are being fast-tracked by almost each vendor on this market.
AI- and machine learning-based vulnerability danger score or scoring ship the insights safety groups want whereas prioritizing and automating patching workflows. The next are 5 of the highest methods AI-driven patch administration is redefining the way forward for cybersecurity:
1. Correct real-time anomaly detection and prediction — a primary line of protection in opposition to machine-speed assaults
Attackers depend on machine-based exploitation of patch vulnerabilities and weaknesses to overwhelm perimeter-based safety at endpoints. Supervised machine studying algorithms, educated on knowledge, establish assault patterns and add them to their data base. With machine identities now outnumbering human identities by an element of 45, attackers see breach alternatives in endpoints, methods and belongings not protected with the most recent patches.
Ivanti’s Mukkamala advised VentureBeat in a latest interview that he envisions patch administration turning into extra automated, with AI copilots offering larger contextual intelligence and prediction accuracy.
“With greater than 160,000 vulnerabilities presently recognized, it’s no marvel that IT and safety professionals overwhelmingly discover patching overly advanced and time-consuming,” Mukkamala mentioned. “This is the reason organizations have to make the most of AI options … to help groups in prioritizing, validating and making use of patches. The way forward for safety is offloading mundane and repetitive duties suited to a machine to AI copilots in order that IT and safety groups can deal with strategic initiatives for the enterprise.”
2. Danger-scoring algorithms that regularly be taught, enhance and scale
Handbook patching tends to fail as a result of it entails balancing many unknown constraints and software program dependencies concurrently. Think about all of the components a safety workforce must cope with. Enterprise software program distributors may be gradual to concern patches. There could have been incomplete regression testing. Patches rushed to clients usually break different components of a mission-critical system, and distributors usually don’t know why. Reminiscence conflicts on endpoints additionally occur usually, degrading endpoint safety.
Danger scoring is invaluable in automating patch administration. Assigning vulnerability danger scores helps prioritize and handle the highest-risk methods and endpoints. Ivanti, Flexera, Tanium and others have developed risk-scoring applied sciences that assist streamline AI-based patch administration.

3. Machine studying is driving positive aspects in real-time patch intelligence
CISOs inform VentureBeat machine studying is without doubt one of the most precious applied sciences for enhancing vulnerability administration throughout large-scale infrastructure. Supervised and unsupervised machine studying algorithms assist obtain sooner SLAs. They enhance the effectivity, scale and velocity of knowledge evaluation and occasion processing. And so they assist with anomaly detection. Machine studying algorithms can present risk knowledge for hundreds of patches utilizing patch intelligence, revealing system vulnerabilities and stability points. All this makes them worthwhile in countering safety threats.
Leaders on this space embrace Automox, Ivanti Neurons for Patch Intelligence, Kaseya, ManageEngine and Tanium.
4. Automating remediation choices saves IT and safety groups worthwhile time whereas enhancing prediction accuracy
Machine studying algorithms enhance prediction accuracy and automate remediation choices by constantly analyzing and studying from telemetry knowledge. One of the fascinating areas on this area of innovation is the fast improvement of the Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS) machine studying mannequin, created with the collective knowledge of 170 consultants.
The EPSS is supposed to assist safety groups handle the rising variety of software program vulnerabilities and establish probably the most harmful ones. Now in its third iteration, the mannequin performs 82% higher than earlier variations. “Remediating vulnerabilities by sooner patching is expensive and may lead astray probably the most lively threats,” writes Gartner in its report Monitoring the Proper Vulnerability Administration Metrics (shopper entry required). “Remediating vulnerabilities through risk-based patching is cheaper and targets probably the most exploitable, business-critical threats.”
5. Contextual understanding of endpoint belongings and identities assigned to them
One other fascinating space of AI-based patch administration innovation is how rapidly distributors are enhancing their use of AI and machine studying to find, stock and patch endpoints that require updates. Every vendor’s strategy is completely different, however they share the purpose of changing the outdated, error-prone, handbook inventory-based strategy. Patch administration and RBVM platform suppliers are fast-tracking new releases that enhance predictive accuracy with improved means to establish which endpoints, machines and methods require patching.
Making use of machine studying algorithms all through the lifecycle
Automating patch administration updates is step one. Subsequent, patch administration methods and RBVM platforms are built-in to enhance model management and alter administration on the utility stage. As supervised and unsupervised machine studying algorithms assist fashions establish potential anomalies early and fine-tune their risk-scoring accuracy, organizations will achieve larger contextual intelligence.
Right this moment, so many organizations are in catch-up mode with respect to patch administration. For these applied sciences to ship their full potential, enterprises should use them to handle complete lifecycles.