(Bloomberg) — Overlook the artificial-intelligence frenzy — the most-exciting commerce on Wall Avenue proper now would possibly simply be betting on boring.
Most Learn from Bloomberg
As winners of the AI growth like Nvidia Corp. energy benchmark inventory gauges to file after file, a much less remarked-upon phenomenon has been unfolding on the coronary heart of the US market: Traders are sinking huge sums into methods whose efficiency hinges on enduring fairness calm.
Often called short-volatility bets, they had been a key issue within the inventory plunge of early 2018 after they worn out in epic trend. Now they’re again in a special guise — and at a a lot, a lot larger scale.
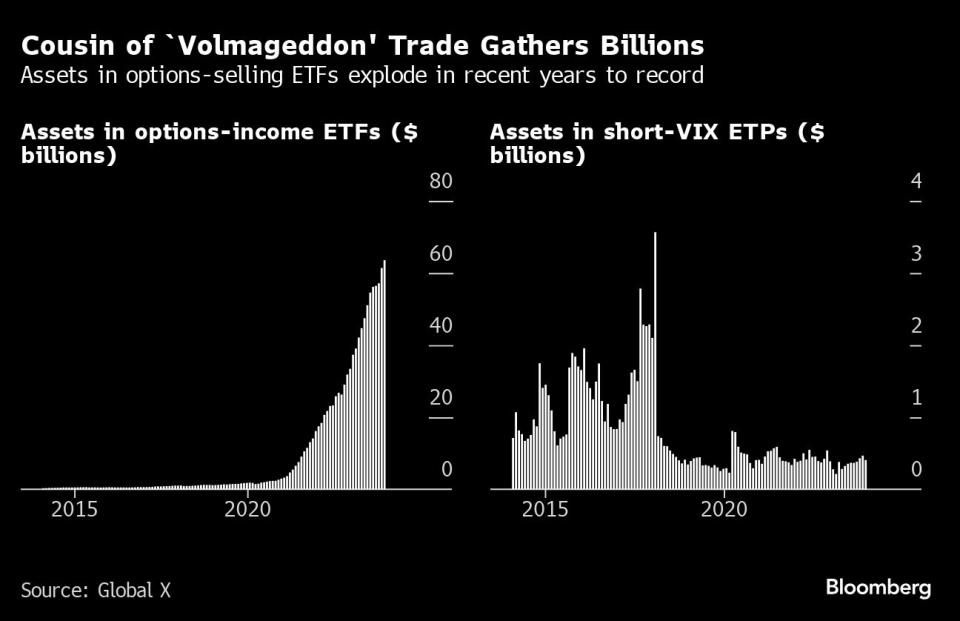
Their new kind largely takes the form of ETFs that promote choices on shares or indexes with the intention to juice returns. Belongings in such merchandise have virtually quadrupled in two years to a file $64 billion, information compiled by World X ETFs present. Their 2018 short-vol counterparts — a small group of funds making direct bets on anticipated volatility — had solely about $2.1 billion earlier than they imploded.
Shorting volatility is an investing strategy that may mint dependable earnings, supplied the market stays tranquil. However with the commerce sucking up property and main occasion dangers just like the US presidential election on the horizon, some buyers are beginning to get nervous.
“The short-vol commerce and its influence is essentially the most constant query we’ve gotten this 12 months,” mentioned Chris Murphy, co-head of derivatives technique at Susquehanna Worldwide Group. “Purchasers wish to know the way a lot of an influence it’s having on markets to allow them to construction their trades higher. However we’ve seen cycles up to now like 2018 and 2020 the place the quick volatility commerce grows till a giant shock blows it up.”
The excellent news for worrywarts is that the structural distinction of the brand new funds modifications the calculus — the earnings ETFs are typically utilizing choices on high of a protracted inventory place, which means that $64 billion isn’t all wagering towards fairness swings. There’s additionally seemingly a better bar for broad contagion than in 2018, because the US market has doubled from six years in the past.
The dangerous information is that the positions — alongside a stack of much less seen short-vol trades by institutional gamers — are suspected of suppressing inventory swings, which invitations but extra bets for calm in a suggestions loop that would someday reverse. The methods are additionally a part of an explosive wider development in derivatives that’s introducing new unpredictability to the market.
‘Anyone Has to Promote’
The buying and selling quantity of US fairness choices surged to a file final 12 months, propelled by a growth in transactions involving contracts which have zero days till expiration, often known as 0DTE. That has enlarged the volatility market, as a result of every by-product quantities to a wager on future worth exercise.
“There principally is a pure elevated demand for choices as a result of retail is speculating utilizing the short-dated lottery-ticket sort of choices,” mentioned Vineer Bhansali, founding father of volatility hedge fund LongTail Alpha LLC. “Anyone has to promote these choices.”
That’s the place many earnings ETFs are available. Somewhat than intentionally betting on market serenity like their short-vol predecessors, the methods make the most of the by-product demand, promoting calls or places to earn further money on an underlying fairness portfolio. It normally means capping a fund’s potential upside, however assuming shares keep calm the contracts expire nugatory and the ETF walks away with a revenue.
Business development lately has been outstanding, and it has largely been pushed by ETFs. On the finish of 2019, there was about $7 billion within the class of by-product earnings funds, based on information compiled by Morningstar Direct, three-quarters of which was in mutual funds. By the top of final 12 months there was $75 billion, virtually 83% of it in ETFs.
However whereas the cash concerned appears to be like larger, derivatives specialists and volatility fund managers are up to now disregarding the chance of one other “Volmageddon,” because the 2018 selloff got here to be identified.

John Marshall, Goldman Sachs Group Inc.’s head of derivatives analysis, mentioned the technique tends to return underneath stress solely when the market rises sharply. A lot of the money is in so-called buy-write ETFs, which take a protracted inventory place and promote name choices for earnings. An enormous rally will increase the possibilities these contracts might be within the cash, obliging the vendor to ship the underlying safety beneath the present buying and selling worth.
“It’s typically a technique that isn’t underneath stress when the market sells off,” Marshall mentioned. “It’s much less of a fear for a volatility spike.”
Earlier than the 2018 blowup, Bhansali at LongTail appropriately foresaw the menace from the rising short-vol commerce. He reckons there’s little hazard of a repeat as a result of this growth is powered by canny merchants merely assembly retail-investor demand for choices, reasonably than making leveraged bets on volatility falling.
In different phrases, the short-vol publicity itself will not be a destabilizing drive, even when such bets are weak to turmoil themselves.
“Sure, there’s potential of instability if there’s a giant market transfer for positive,” Bhansali mentioned. However “anyone promoting these choices doesn’t essentially imply that there’s an enormous unhedged quick base,” he mentioned.
Nonetheless, quantifying any potential threat is tough as a result of even figuring out the precise dimension of the short-vol commerce is a problem. Methods can tackle varied shapes past the comparatively easy earnings funds, and plenty of transactions happen on Wall Avenue buying and selling desks the place info will not be obtainable to the general public.
To many, the earnings ETF growth is a tell-tale signal of one thing larger going down beneath the floor.
“Once you’re seeing one thing happening publicly, there’s most likely 5 to 10 occasions that happening privately that you just don’t see immediately,” mentioned Steve Richey, a portfolio supervisor at QVR Advisors, a volatility hedge fund.
Dispersion Doubts
These unseen bets embody a big chunk of quantitative funding methods — structured merchandise offered by banks that mimic quant trades.
In line with PremiaLab, which tracks QIS choices throughout 18 banks, fairness short-vol trades returned 8.9% within the US final 12 months and wound up accounting for roughly 28% of latest methods added to the platform over the previous 12 months. Their notional worth is unknown, however consultancy Albourne Companions estimated final 12 months that QIS trades total command about $370 billion.
Hedge funds gaming relative volatility are additionally feeding the growth. Some of the infamous short-vol bets is an unique choices technique often known as the dispersion commerce. Using varied complicated choices overlays, it quantities to being lengthy volatility in a basket of shares whereas wagering towards the swings of an index just like the S&P 500. To work, it wants the broader market to remain subdued, or not less than expertise much less turbulence than the person shares.
With the S&P 500 steadily going up whereas inventory returns diverged broadly lately, the technique has flourished. As soon as once more it’s tough to measure the scale of the commerce, however it’s widespread sufficient that Cboe World Markets plans to listing a futures product tied to the Cboe S&P 500 Dispersion Index this 12 months.
That rising reputation, mixed with leverage and a scarcity of transparency, has prompted Kevin Muir of the MacroTourist weblog to warn {that a} market selloff may upset the commerce, forcing an unwinding of positions that would additional exacerbate the rout.
“It worries me as a result of the dispersion commerce has all of the hallmarks of a crisis-in-the-making,” Muir wrote. It’s “precisely the form of subtle, extremely levered commerce the place everybody assumes ‘these guys are math whizzes – we don’t want to fret about them blowing up as a result of they’re hedged,’” he mentioned.
To get an concept of how a lot short-vol publicity is on the market, market gamers can usually be discovered including up what’s often known as vega. That’s a measure of how delicate an choice is to modifications in volatility.
At Ambrus Group, one other volatility hedge fund, an inside measure of vega aggregates choices exercise for the S&P 500 Index, the Cboe Volatility Index — a gauge of implied worth swings within the US fairness benchmark also referred to as the VIX — and the SPDR S&P 500 ETF Belief (SPY). Kris Sidial, co-chief funding officer, mentioned in January the web quick vega publicity was two occasions bigger than within the run-up to the 2018 rout.


Meaning a 1-point enhance in volatility may incur notional losses double these skilled six years in the past. The massive fear: Panicked buyers unwinding positions as their losses mount may gasoline extra volatility, which causes extra losses and extra promoting.
Such a state of affairs raises the chance of introducing one other draw back accelerant within the form of the sellers and market makers who’re normally on the opposite aspect of derivatives transactions. They don’t have their very own directional view, so goal to keep up a impartial stance by shopping for and promoting shares, futures or choices that offset one another.
In a giant market decline — when sellers all of the sudden discover themselves promoting excessive portions of choices that defend or profit from the rout — it tends to place them in what’s referred to as “quick gamma.” The dynamics are complicated, however the upshot is that to neutralize their publicity sellers must promote into the downdraft, compounding the drop.
For now, the short-vol commerce’s proliferation has been proposed as one cause why the VIX has stayed eerily low up to now 12 months regardless of two ongoing main geopolitical conflicts and the Federal Reserve’s most aggressive financial tightening in many years. That’s as a result of in present circumstances, sellers are in a “lengthy gamma” place that typically sees them shopping for when shares go down and promoting after they go up — dampening swings.
In its newest quarterly evaluation revealed final week, the Financial institution for Worldwide Settlements mentioned that dynamic was the seemingly cause behind the compression of volatility given the growth in methods that eke out earnings from promoting choices. “The meteoric rise of yield-enhancing structured merchandise linked to the S&P 500 during the last two years has gone hand in hand with the drop of VIX over the identical interval,” researchers wrote.
There are good various causes for the calm. The inventory market has steadily floor larger as neither the Fed nor the US economic system delivered any main shocks over the previous 12 months. It’s additionally potential that, with so many bets now positioned utilizing short-dated choices, the VIX not captures all of the motion since it’s calculated utilizing contracts about one month out.
But QVR Advisors additionally sees the footprints of the growth in vol-selling. The diploma of swings priced into S&P 500 choices — so-called implied volatility — has drifted decrease over time versus how a lot the index really strikes round, its information present. The idea is that cash managers flooding the market with contracts to generate earnings are placing a lid on implied volatility — which in spite of everything is successfully a gauge of the price of choices. The hedge fund has lately launched a technique in search of to make the most of low-cost derivatives that profit from giant swings within the S&P 500, whether or not up or down.
“Put up pandemic, we’ve seen elementary and technical causes for volatility suppression,” mentioned Amy Wu Silverman, head of derivatives technique at RBC Capital Markets. “Whereas I feel that continues, it turns into an increasing number of tough to be quick volatility from right here.”
Loads of macro components exist with the potential to disrupt the inventory market’s regular march larger, together with the continued wars in Ukraine and Gaza, lingering inflation and the American elections. And whereas vol-selling methods have supplied buyers with good points traditionally, they’ve a fame for his or her function in compounding routs.
Essentially the most well-known episode passed off in February 2018, when a downturn within the S&P 500 sparked a surge within the VIX, wiping out billions of {dollars} in trades betting towards volatility that had constructed up throughout years of relative calm. Among the many largest casualties was the VelocityShares Each day Inverse VIX Quick-Time period notice (XIV), whose property shrank from $1.9 billion to $63 million in a single session.
A catalyst has but to emerge to set off a repeat. Even when the Israel-Hamas conflict broke out in October or the US reported hotter-than-expected inflation for January, the market remained serene. The VIX has stayed beneath its historic common of 20 for nearly 5 months, a stretch of dormancy that was exceeded solely two occasions since 2018.
To Tobias Hekster, co-chief funding officer at volatility hedge fund True Accomplice Capital, that enduring interval of calm presents little reassurance.
“You’re assuming a threat — the truth that that threat hasn’t materialized over the previous one and a half years does not imply it would not exist,” Hekster mentioned. “If one thing journeys up the market, the longer the volatility has been suppressed, the extra violent the response.”
Most Learn from Bloomberg Businessweek
©2024 Bloomberg L.P.

