(Bloomberg) — A way of conviction that bonds needs to be purchased helps fund managers put the worst yr in a era behind them.
Most Learn from Bloomberg
Even because the Federal Reserve has made clear it intends to boost charges additional to insure continued progress on inflation, and that it’s not considering the eventual fee cuts merchants are pricing in, buyers are already being rewarded for seeing worth within the Treasury market. With this week’s improve to 4.25%-4.5%, the central financial institution’s vary for the federal funds fee exceeds the highest-yielding Treasury securities — a warning to buyers towards ready any longer to purchase.
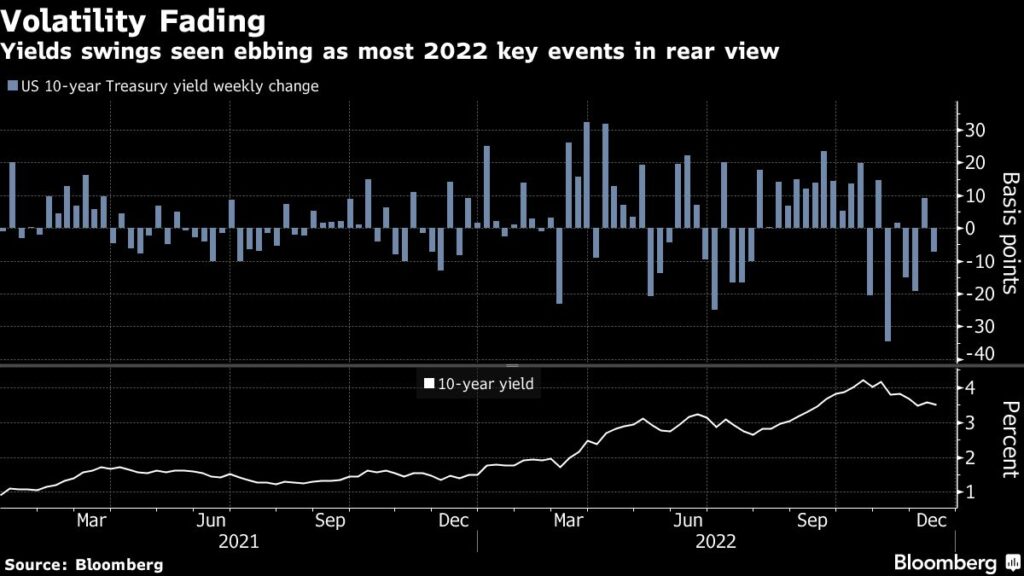
On a number of events this week, intraday spikes in yield dissipated shortly, an indication that consumers are pouncing on them. The primary occurred after the Fed resolution Wednesday, spurred by coverage makers’ upwardly revised median forecasts for the eventual peak within the coverage fee and for inflation. Over the following two days, a deep selloff in euro-zone authorities bonds sparked by hawkish European Central Financial institution commentary triggered solely non permanent cheapening in US charges. A steep drop in Treasury volatility this week after the Fed resolution boosted investor confidence that yields received’t attain new highs.
The curiosity in shopping for bonds displays the view that inflation in all probability has peaked and can fall sharply, even when the Fed isn’t prepared to attract that conclusion. Additionally that the 4 share level improve within the coverage fee since March is sowing the seeds of a recession that can lead finally to fee cuts, if not in 2023 then in 2024.
“We imagine that the outlook for 2023 is beginning to brighten,” mentioned Marion Le Morhedec, world head of fastened earnings at AXA Funding Managers SA. The rise in charges we’ve seen this yr “provides to the attractiveness of the bond market” and central financial institution tightening “appears to be principally behind us.”
Apart from the two-year be aware’s — extra delicate than longer-maturity yields to the extent of the Fed’s coverage fee — charges throughout the Treasury spectrum are again beneath 4%. The 2-year peaked at practically 4.80% final month, the 10-year close to 4.34% in October, each multiyear highs. The corresponding stoop in bond costs erased as a lot as 15% of the worth of the Bloomberg Treasury Index this yr. Whereas the loss has been pared to about 11%, it’s nonetheless the worst within the index’s five-decade historical past.
The ten-year be aware’s yield approached 3.40% this month, aided by indicators of moderating inflation within the October and November shopper value index reviews, and Fed Chair Jerome Powell previewing the slower tempo of fee hikes the central financial institution adopted with its half-point hike on Dec. 14.
To make sure, the drop in yields from their highs raises the stakes for buyers who assume now’s the time to purchase. The brand new median forecasts of Fed coverage makers launched after this week’s assembly confirmed they anticipate the next peak for the fed funds fee of 5.1% subsequent yr to deal with an elevated core inflation forecast to three.5%.
Powell within the information convention following the assembly emphasised that as a result of the labor market has but to indicate any significant indicators of softening, its unclear how lengthy the coverage fee might want to stay at its eventual peak. On the similar time, coverage makers’ median forecasts for 2024 embody a decline within the funds fee to 4.125%.
“A ten-year at 3.5% does look just a little too low, however on the similar time it’s troublesome to see upward strain on authorities bond yields when inflation is beginning to co-operate,” mentioned Andrzej Skiba, head of the BlueBay US fastened earnings workforce at RBC World Asset Administration.
Subsequent week, private earnings and spending information for November are anticipated to indicate a decline within the core inflation fee to 4.6%, the bottom since October 2021. The College of Michigan’s December sentiment survey, to be revised subsequent week, discovered customers anticipate 4.6% inflation over the following yr, additionally the bottom in additional than a yr.
Market-implied inflation expectations even have waned, with the breakeven fee for five-year Treasury inflation-protected securities approaching its year-to-date lows round 2.20%. That means buyers believe the Fed will reach wrestling the CPI fee, 7.1% in November, down farther from its June peak of 9.1%.
San Francisco Fed President Mary Daly, talking Friday, mentioned the central financial institution stays removed from its value stability aim and has “an extended approach to go.” Bond merchants weren’t fazed.
Seasonal dynamics complicate the evaluation, nonetheless, mentioned Michael de Go, head of linear charges at Citadel Securities.
The bullish bond market tone “could mirror year-end flows as cash strikes into bonds amid low liquidity,” he mentioned.
However after 400 foundation factors of fee hikes, a hawkish Fed not poses the identical diploma of hazard to bond buyers it as soon as did, enabling them to attract completely different conclusions.
“The Fed has largely caught as much as the scenario on the bottom,” de Go mentioned. “The market thinks the financial system and labor market will deteriorate way more materially than the Fed does.”
What to Watch
-
Financial calendar:
-
Dec. 19: NAHB housing market index
-
Dec. 20: Housing begins
-
Dec. 21: MBA mortgage functions; present account stability; present residence gross sales; Convention Board shopper confidence
-
Dec. 22: 3Q GDP closing revision; weekly jobless claims; Main Index; Kansas Metropolis Fed manufacturing exercise
-
Dec. 23: Private earnings and spending; sturdy items orders; new residence gross sales; College of Michigan sentiment survey
-
-
Fed calendar:
-
Public sale calendar:
-
Dec. 19: 13-week; 26-week payments
-
Dec. 21: 17-week payments; 20-year bond
-
Dec. 22: 4-week, 8-week payments; 5yr TIPS
-
Most Learn from Bloomberg Businessweek
©2022 Bloomberg L.P.