If you happen to’ve ever been admitted to hospital or visited an emergency division, you have doubtless had an electrocardiogram, or ECG, a regular take a look at involving tiny electrodes taped to your chest that checks your coronary heart’s rhythm and electrical exercise.
Hospital ECGs are normally learn by a health care provider or nurse at your bedside, however now researchers are utilizing synthetic intelligence to glean much more info from these outcomes to enhance your care and the health-care system all of sudden.
In not too long ago printed findings, the analysis group constructed and skilled machine studying packages based mostly on 1.6 million ECGs carried out on 244,077 sufferers in northern Alberta between 2007 and 2020.
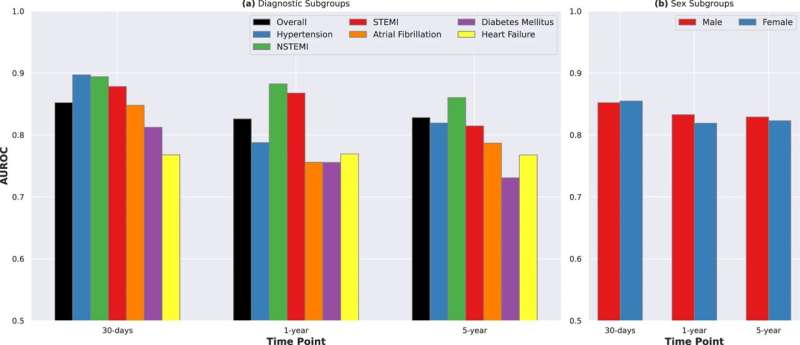
The algorithm predicted the danger of dying from that time for every affected person from all causes inside one month, one yr and 5 years with an 85 p.c accuracy charge, sorting sufferers into 5 classes from lowest to highest threat. The predictions have been much more correct when demographic info (age and intercourse) and 6 commonplace laboratory blood take a look at outcomes have been included.
The examine is a proof-of-concept for utilizing routinely collected knowledge to enhance particular person care and permit the health-care system to “study” because it goes, in response to principal investigator Padma Kaul, professor of medication and co-director of the Canadian VIGOUR Centre.
“We needed to know whether or not we may use new strategies like synthetic intelligence and machine studying to investigate the info and establish sufferers who’re at increased threat for mortality,” Kaul explains. “These findings illustrate how machine studying fashions may be employed to transform knowledge collected routinely in medical follow to data that can be utilized to reinforce decision-making on the level of care as a part of a studying health-care system.”
A clinician will order an electrocardiogram when you’ve got hypertension or signs of coronary heart illness, similar to chest ache, shortness of breath or an irregular heartbeat. The primary part of the examine examined ECG leads to all sufferers, however Kaul and her group hope to refine these fashions for explicit subgroups of sufferers. Additionally they plan to focus the predictions past all-cause mortality to look particularly at heart-related causes of dying.
“There’s a massive push to see how we are able to use AI to enhance the supply of well being care,” says Kaul. The benefit of utilizing high-powered computing is that, in contrast to people, it could possibly see the patterns in a large number of information factors directly, she says. “We need to take knowledge generated by the health-care system, convert it into data and feed it again into the system in order that we are able to enhance care and outcomes. That is the definition of a studying health-care system.”
The examine is printed within the journal npj Digital Drugs.
Extra info:
Weijie Solar et al, In direction of synthetic intelligence-based studying well being system for population-level mortality prediction utilizing electrocardiograms, npj Digital Drugs (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41746-023-00765-3
College of Alberta
Quotation:
Machine studying packages predict threat of dying based mostly on outcomes from routine hospital exams (2023, March 21)
retrieved 21 March 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-03-machine-death-based-results-routine.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.