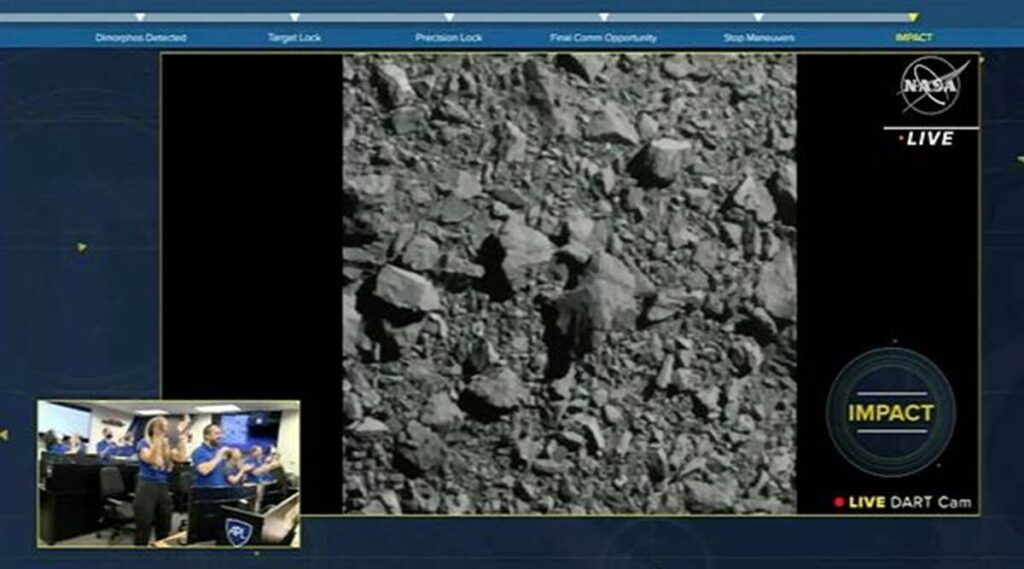
A NASA spacecraft rammed an asteroid at blistering velocity Monday in an unprecedented gown rehearsal for the day a killer rock menaces Earth.
The galactic grand slam occurred at a innocent asteroid 7 million miles (9.6 million kilometers) away, with the spacecraft named Dart plowing into the small house rock at 14,000 mph (22,500 kph). Scientists anticipated the influence to carve out a crater, hurl streams of rocks and dust into house and, most significantly, alter the asteroid’s orbit. Telescopes around the globe and in house aimed on the similar level within the sky to seize the spectacle. Although the influence was instantly apparent — Dart’s radio sign abruptly ceased — it is going to be days and even weeks to find out how a lot the asteroid’s path was modified.
The $325 million mission was the primary try and shift the place of an asteroid or some other pure object in house.
“No, this isn’t a film plot,” NASA Administrator Invoice Nelson tweeted earlier within the day.
”We’ve all seen it on motion pictures like ‘Armageddon,’ however the real-life stakes are excessive,” he mentioned in a prerecorded video.Monday’s goal: a 525-foot (160-meter) asteroid named Dimorphos. It’s really a moonlet of Didymos, Greek for twin, a fast-spinning asteroid 5 instances greater that flung off the fabric that shaped the junior associate.
The pair have been orbiting the solar for eons with out threatening Earth, making them ultimate save-the-world take a look at candidates.Launched final November, the merchandising machine-size Dart — brief for Double Asteroid Redirection Take a look at — navigated to its goal utilizing new expertise developed by Johns Hopkins College’s Utilized Physics Laboratory, the spacecraft builder and mission supervisor. Dart’s on-board digicam, a key a part of this good navigation system, caught sight of Dimorphos barely an hour earlier than influence. “Woo hoo,” exclaimed Johns Hopkins mission programs engineer Elena Adams. “We’re seeing Dimorphos, so fantastic, fantastic.” With a picture beaming again to Earth each second, Adams and different floor controllers in Laurel, Maryland, watched with rising pleasure as Dimorphos loomed bigger and bigger within the area of view alongside its greater companion. A mini satellite tv for pc adopted a couple of minutes behind to take pictures of the influence. The Italian Cubesat was launched from Dart two weeks in the past.
Scientists insisted Dart wouldn’t shatter Dimorphos. The spacecraft packed a scant 1,260 kilos (570 kilograms), in contrast with the asteroid’s 11 billion kilos (5 billion kilograms). However that ought to be a lot to shrink its 11-hour, 55-minute orbit round Didymos.The influence ought to pare 10 minutes off that, however telescopes will want wherever from just a few days to almost a month to confirm the brand new orbit. The anticipated orbital shift of 1% may not sound like a lot, scientists famous. However they careworn it could quantity to a big change over years.
Planetary protection consultants favor nudging a threatening asteroid or comet out of the way in which, given sufficient lead time, moderately than blowing it up and creating a number of items that would rain down on Earth. A number of impactors may be wanted for large house rocks or a mix of impactors and so-called gravity tractors, not-yet-invented gadgets that might use their very own gravity to drag an asteroid right into a safer orbit.
“The dinosaurs didn’t have an area program to assist them know what was coming, however we do,” NASA’s senior local weather adviser Katherine Calvin mentioned, referring to the mass extinction 66 million years in the past believed to have been attributable to a serious asteroid influence, volcanic eruptions or each.The non-profit B612 Basis, devoted to defending Earth from asteroid strikes, has been pushing for influence exams like Dart since its founding by astronauts and physicists 20 years in the past. Monday’s feat apart, the world should do a greater job of figuring out the numerous house rocks lurking on the market, warned the inspiration’s government director, Ed Lu, a former astronaut. Considerably lower than half of the estimated 25,000 near-Earth objects within the lethal 460-foot (140-meter) vary have been found, in accordance with NASA. And fewer than 1% of the thousands and thousands of smaller asteroids, able to widespread accidents, are identified.
The Vera Rubin Observatory, nearing completion in Chile by the Nationwide Science Basis and U.S. Power Division, guarantees to revolutionize the sphere of asteroid discovery, Lu famous. Discovering and monitoring asteroids, “That’s nonetheless the secret right here. That’s the factor that has to occur so as to defend the Earth,” he mentioned.