LONDON, Could 11 (Reuters) – Inflation is easing however main central banks stay very a lot in price hike mode, with the Financial institution of England delivering its twelfth straight rate of interest enhance on Thursday.
Monetary markets nonetheless imagine probably the most aggressive tightening cycle in many years might quickly be over, a way elevated by latest banking sector turmoil that has added to world recession dangers.
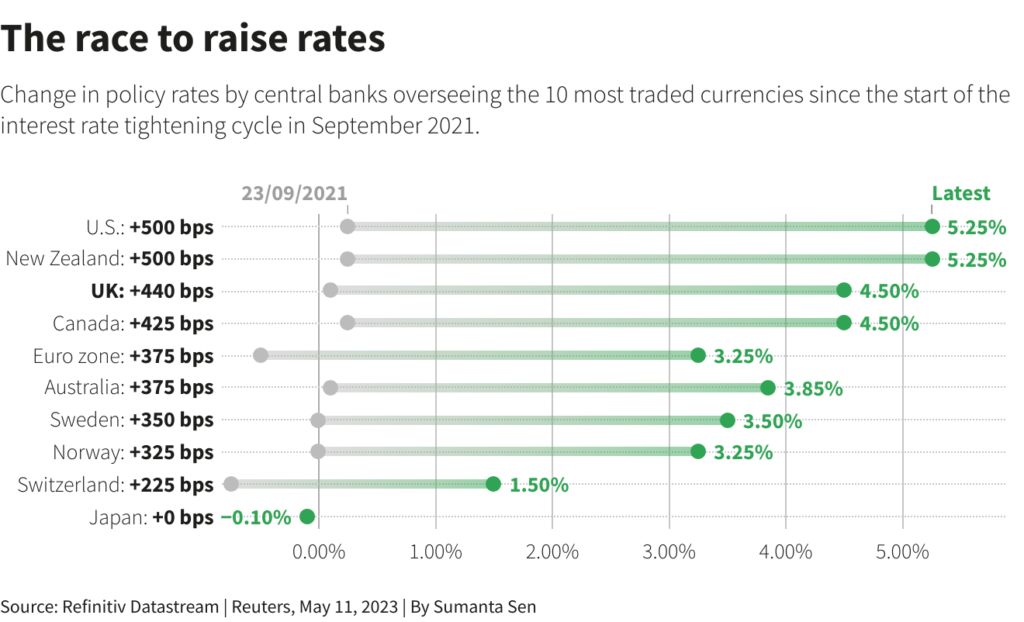
To this point, 10 developed economies have raised charges by a mixed 3,515 foundation factors (bps) on this cycle.
Japan is the holdout dove.
Here is a have a look at the place policymakers stand, from hawkish to dovish.
1) UNITED STATES
The Fed raised charges by 1 / 4 level to five.00-5.25% final Wednesday, persevering with its most aggressive collection of hikes because the Nineteen Eighties.
The U.S. central financial institution provided markets some succour, dropping from its coverage assertion language that it “anticipates” additional price will increase.
Fed chief Jerome Powell mentioned inflation stays the chief concern, and that it’s subsequently too quickly to say with certainty that the rate-hike cycle is over.
2) NEW ZEALAND
The Reserve Financial institution of New Zealand shocked markets in April by unexpectedly elevating its money price by 50 bps to five.25%, the very best in over 14 years. Not one economist polled by Reuters had predicted the transfer.
The central financial institution mentioned inflation was nonetheless “too excessive” with employment past “most sustainable ranges”. Analysts revised their forecasts for the height in rates of interest as much as 5.5%.
3) CANADA
The Financial institution of Canada in March grew to become the primary main central financial institution to halt financial tightening throughout this cycle.
The BoC’s key in a single day price stays at 4.50%, with the purpose to carry it there so long as inflation drops to three% at about mid-year.
Market members imagine there will be no change till subsequent yr, based on a central financial institution survey launched on April 24.
4) BRITAIN
The Financial institution of England raised its key rate of interest by 25 foundation factors to 4.5% as anticipated on Thursday, searching for to curb the very best inflation in any main economic system.
The central financial institution mentioned it not expects a recession, however anticipates inflation will take longer to fall than it had hoped, largely as a consequence of unexpectedly massive and chronic rises in meals costs.
5) AUSTRALIA
Australia’s central financial institution confounded expectations of a pause with a 25 bps hike in Could.
The money price now stands at a 12-year excessive of three.85% and the RBA mentioned “some additional tightening” could also be required to make sure inflation returns to focus on in a “affordable timeframe”.
6) NORWAY
Norway’s central financial institution raised its primary rate of interest by 25 bps final Thursday to three.25%. It mentioned one other hike in June was possible – and that extra may very well be wanted if the forex stays weak.
The Norwegian crown has had a horrible yr, with the greenback up virtually 9% towards the forex in 2023. In the meantime, inflation stays sizzling, with the core price selecting as much as 6.3% in April.
7) EURO ZONE
The ECB raised its deposit price by 25 bps final Thursday to three.25%, its seventh successive hike however the smallest because it began lifting charges final summer season.
The central financial institution saved its choices open on future strikes because it continues combating stubbornly excessive inflation within the euro zone.
President Christine Lagarde mentioned whereas financial coverage is little doubt restrictive, it’s not but “sufficiently restrictive”, noting that the “inflation outlook is simply too excessive and has been so for too lengthy.”
8) SWEDEN
The Riksbank raised borrowing prices by 50 bps in April to three.5% however mentioned it was almost completed with coverage tightening, prompting a drop within the Swedish crown.
Sweden’s underlying price of inflation stripping out vitality costs eased to eight.9% in March however stays properly above the central financial institution’s 2% goal.
Whereas traders had beforehand anticipated charges to peak at 4%, the Riksbank recommended just one extra 25 bps hike is probably going.
9) SWITZERLAND
The Swiss Nationwide Financial institution raised its primary rate of interest by 50 bps in March to 1.5%, saying UBS’s emergency takeover of Credit score Suisse had “put a halt” to the possibility of a banking disaster.
Swiss inflation cooled to 2.6% in April, from 3.4% in February, however remained above the SNB’s goal band for the thirteenth straight month.
Merchants count on an additional 25 bp hike in June, market pricing suggests.
10) JAPAN
The Financial institution of Japan appears to be like set to stay the world’s most dovish central financial institution below new governor Kazuo Ueda.
At Ueda’s first assembly in late April the BOJ maintained its extremely low charges and its yield curve management coverage that caps rates of interest on long run authorities bonds.
The BOJ additionally introduced a plan to assessment its previous financial coverage strikes however mentioned this train will take one-and-a-half years.
Reporting by Samuel Indyk, Nell Mackenzie, Dhara Ranasinghe, Alun John, Naomi Rovnick, Harry Robertson and Chiara Elisei; Graphics by Vincent Flasseur, Sumanta Sen and Pasit Kongkunakornkul and Riddhima Talwani; Modifying by Catherine Evans
: .