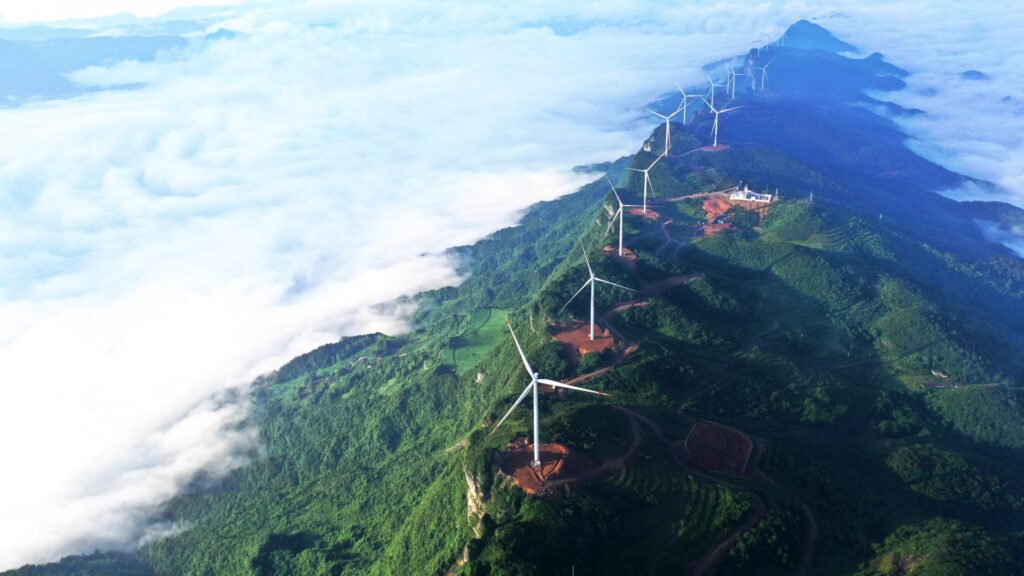
China goals to succeed in peak carbon emissions in 2030. Pictured here’s a wind farm in Chongqing in southwest China, on June 28, 2022.
Future Publishing | Future Publishing | Getty Photographs
BEIJING — China says it desires to be carbon impartial by 2060 — and people acknowledged ambitions are spawning corporations that might in the future develop into international leaders of their fields.
Two years in the past, Chinese language President Xi Jinping formally introduced the world’s second largest economic system would attempt for peak carbon emissions in 2030, and carbon neutrality in 2060.
To be carbon impartial means the quantity of carbon dioxide emitted by the entire nation might be offset in different methods. It additionally means there should not?/will not? be any improve in greenhouse emissions in China after 2030.
Whereas the nation struggles to wean itself off coal, analysts mentioned Beijing’s top-level emphasis on local weather has fueled a coverage push to attempt to assist companies targeted on renewable power and decreasing carbon emissions.
“China’s already a pacesetter in so many elements of the decarbonization effort,” mentioned Norman Waite, power finance analyst on the Institute for Vitality Economics and Monetary Evaluation (IEEFA).
“They’re both main or proper within the pack with everyone else within the efforts to decarbonize. It is not a one- or two-company effort. This can be a bunch of corporations who’re urgent ahead,” he mentioned.
Abroad growth
Electrical automobiles and batteries have been an apparent progress space, with Chinese language EV makers increasing their companies past China.
Chinese language electrical automobile big and battery maker BYD launched passenger automobiles for Europe in late September, whereas start-up Nio is ready to carry its European launch occasion in Berlin in early October.
Applied sciences to retailer and transmit energy generated through renewable sources are one other space that analysts are watching.

“Extra of the Chinese language corporations are attending to the dimensions in China that they begin to exit as nicely and set up partnerships overseas” in power storage, mentioned Johan Annell, accomplice at Asia Perspective, a consulting agency that works primarily with Northern European corporations working in East and Southeast Asia.
In power effectivity, gear for heating and cooling, Annell mentioned, “you are additionally getting a variety of Chinese language corporations going out and beginning to win enterprise, notably within the nations surrounding China” — resembling Mongolia and Kazakhstan.
Rising chief in offshore wind?
The offshore wind sector is one other discipline that might see an rising Chinese language chief.
Offshore wind is a renewable power that makes use of generators in coastal waters — a lot of which might be put in close to the world’s largest city facilities, IEEFA’s Waite mentioned in a September report.
China’s leaders additionally acknowledge that, in the long run, China’s growth won’t be economically sustainable – and therefore politically and socially sustainable – till additionally it is environmentally so.
Mingyang Sensible Vitality, already a pacesetter in offshore wind energy in China, “seems poised to disrupt worldwide, non-Chinese language markets at a weak time for established rivals,” Waite mentioned. He famous the corporate can sort out abroad markets with its robust stability sheet, massive manufacturing capability and probably aggressive pricing energy.
The trade’s three international gamers — Siemens Gamesa Renewable Vitality, Denmark’s Vestas Wind System and Normal Electrical — “are racking up losses, and solely Vestas is doing so with out the additional stress of an imminent restructuring,” he mentioned.
Vestas mentioned it does not touch upon its rivals, and the 2 different corporations didn’t reply to CNBC’s request for remark.

In December, Mingyang signed a memorandum of understanding to construct a manufacturing facility within the U.Okay. and discover choices for coming into the native British market.
The corporate’s different initiatives or contracts embrace companions in Italy, Japan and Vietnam, Waite mentioned.
The U.Okay. and the remainder of Europe are every anticipated so as to add about 10 gigawatts of offshore wind energy within the subsequent three years, in keeping with IEEFA Analysis.
Within the following 5 years, that capability is ready to triple within the U.Okay., and improve by five-fold within the European mainland to about 60 gigawatts, the report mentioned.
‘New infrastructure funding’
For Chinese language corporations, aligning with the nation’s carbon neutrality theme matches nicely with Beijing’s different directives — for enhancing innovation, transferring into higher-end industrial manufacturing and boosting non-traditional infrastructure funding, mentioned Bruce Pang, chief economist and head of analysis for Larger China at JLL.
“In case you are a rational company of the native authorities, your actions underneath the rationale might be targeted [on projects] underneath the title of latest infrastructure funding,” he mentioned.
Nationwide safety is one other issue driving China’s concentrate on growing power sources.
“Vitality safety is given extra of a precedence due to the financial challenges and the socioeconomic challenges,” mentioned Seungjoo Ro, CLSA’s head of ESG analysis, sustainability and company governance analysis.
Ro identified that there are nonetheless 38 years to go in China’s carbon impartial roadmap, and it is nonetheless not completely clear how buyers can measure potential share worth returns primarily based solely on climate-related measures proper now.
Not a simple street forward
In observe, some $22 trillion are required to realize China’s bold carbon targets, in keeping with a report from the World Financial Discussion board and Oliver Wyman.
“To realize its bold carbon peak and carbon neutrality targets, China wants to shut an annual funding hole of about RMB1.1 trillion ($170 billion),” the summer season report identified. “It could solely accomplish that if it manages to develop much more refined inexperienced financing schemes.”
And if Chinese language corporations need to play a task in international efforts to succeed in atmosphere targets, some variations between native requirements should be resolved with worldwide ones, mentioned Kelly Tian, monetary services-focused principal at Oliver Wyman.
The final two years present how Chinese language leaders nonetheless battle to stability progress and financial pursuits with attaining local weather targets, particularly in an economic system the place coal is the dominant power supply.
Overenthusiastic measures to pressure native areas to chop carbon emissions final 12 months resulted in an influence scarcity that disrupted manufacturing facility manufacturing.
China ended up including coal manufacturing capability this 12 months, serving to the nation stave off comparable energy shortages, regardless of excessive dry and scorching climate in elements of the nation, mentioned Cory Combs, affiliate director at analysis and consulting agency Trivium China, in a September report printed by Asia Society Coverage Institute.
Even when the carbon directives come from the highest management, Combs mentioned there’s nonetheless rigidity between short-term and longer-term financial pursuits that may seemingly final by way of the approaching decade.
Lowering that rigidity will assist China cut back carbon emissions, he mentioned. “However China’s leaders additionally acknowledge that, in the long run, China’s growth won’t be economically sustainable – and therefore politically and socially sustainable – till additionally it is environmentally so.”
China’s state-run media has promoted environmental enhancements throughout the nation. And after years of a number of the worst air air pollution on the planet, circumstances in Beijing have improved a lot within the final 12 months that locals can regularly see far-off mountains and stars from the middle of town.


