FRANKFURT, Could 26 (Reuters) – As banks got here below mounting strain in March, Deutsche Financial institution (DBKGn.DE) used huge trades to present its money buffers a short lived increase, using a technique that European regulators have raised issues over, two sources aware of the state of affairs stated.
Deutsche swapped billions of euros in securities for money and authorities bonds, the sources informed Reuters, which depend in direction of its liquidity protection ratio (LCR). That is meant to find out the extent of a financial institution’s entry to prepared money to fund outflows similar to depositor withdrawals.
Whereas a reliable banking apply, the transfer underscored concern at Deutsche over the broader turmoil. Having a big money pile would have reassured traders and shoppers after Credit score Suisse and a variety of U.S. banks suffered deposit runs.
The trades caught the eye of European Central Financial institution (ECB) supervisors, who questioned Germany’s largest lender about them throughout routine exchanges, the sources stated.
Even with out the trades, Deutsche would have far exceeded a 100% LCR regulatory requirement and overshot its personal goal, the sources stated, including that its liquidity isn’t a priority.
The essential factor for the ECB, they stated, is to determine how a lot liquidity a financial institution has at that given second, in addition to what it plans on having within the following months.
The problem is that liquidity can evaporate if short-term trades should not renewed, clouding the longer-term view.
“These items can shift round in a short time however as a supervisor I’d be apprehensive in the event that they had been doing this on the finish of quarter, simply to look nicer, and I’d wish to look into it,” stated Thorsten Beck, Director of the Florence Faculty of Banking and Finance and a co-chair of the Advisory Scientific Committee of the European Systemic Danger Board.
Deutsche’s use of such trades to enhance its liquidity place on the peak of the current banking turmoil has not been beforehand reported and conversations with the regulator are confidential.
The apply isn’t uncommon amongst huge banks, but it surely was flagged by the ECB in a 2019 stress check as a method for making a financial institution look stronger.
Deutsche’s trades allowed it to put up a rise in its LCR in March, serving to chief govt Christian Stitching reward the financial institution’s “resilience” and “strong basis” to analysts when presenting the first-quarter determine in April.
Deutsche “actively manages to a conservative liquidity profile throughout a variety of liquidity metrics,” a spokesperson informed Reuters. Its liquidity degree displays “prudent steering in an unsure market setting” and the late March enhance was “primarily pushed by seasonal actions,” they added.
An ECB spokesperson declined to remark.
‘SOLID FOUNDATIONS’
March was a tense interval for banks. Days after Switzerland engineered the rescue of Credit score Suisse, Deutsche’s clients started withdrawing deposits, its executives later stated, whereas shares within the financial institution dropped as a lot as 15% on a single day.
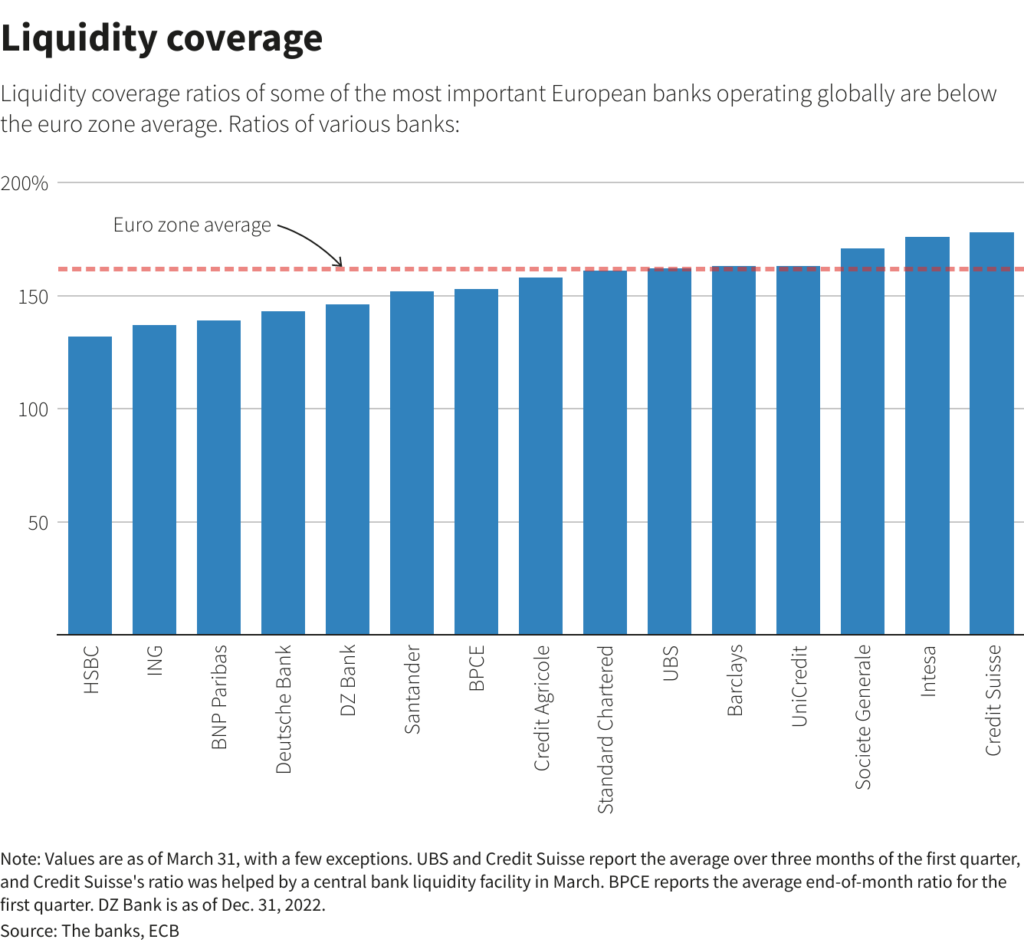
One concern out there on the time was whether or not banks had sufficient money readily available to satisfy the calls for of depositors. Euro zone banks are required to have an LCR of not less than 100%, that means they’ve sufficient liquid belongings to cowl a month’s price of outflows.
Deutsche’s trades helped it increase its LCR to 143% at March 31, its first-quarter earnings report revealed in April confirmed.
The determine stood at 137% on March 23, it had reported in a submitting on the time, in an uncommon transfer meant to calm markets.
The sharp enhance got here as a shock, nevertheless, after Deutsche stated in February that it will steer the LCR ratio decrease in direction of its 130% goal throughout the yr.
Such short-term fixes, which generate huge LCR strikes, are prone to increase recent questions from regulators and analysts concerning the reliability of necessities launched after the worldwide monetary disaster of 2008.
Credit score Suisse stated it had an LCR of round 150%, calculated utilizing a three-month common, lower than every week earlier than being declared non-viable by Swiss authorities and brought over by UBS.
One supply stated that if there may be one factor that the ECB had discovered from the speedy demise of Credit score Suisse is that the LCR is an unreliable indicator as deposits can disappear in a single day.
The 2019 ECB stress check on liquidity discovered that a variety of banks had been utilizing “collateral swaps aimed toward enhancing the amount (or) high quality of the LCR buffer”.
One weak spot the ECB discovered then was {that a} quantity reported a “pronounced” liquidity drop after day 30, which can consequence from ‘optimisation’ methods.
It additionally stated that the technique had change into a supply of “interconnectedness amongst banks”, which regulators see as a supply of systemic danger for the sector.
Hans-Peter Burghof, a professor of banking and finance at Germany’s College of Hohenheim, stated the controversy concerning the usefulness of liquidity metrics has been happening for many years.
“Belief cannot be measured with numbers,” he stated. “If I had been a regulator, I’d hate it,” Burghof added of practices similar to banks elevating their LCRs utilizing swaps and different trades.
Enhancing by Elisa Martinuzzi, Paritosh Bansal and Alexander Smith
: .