WASHINGTON – Fallout from the U.S. banking disaster is more likely to tilt the economic system into recession later this 12 months, in accordance with Federal Reserve paperwork launched Wednesday.
Minutes from the March assembly of the Federal Open Market Committee included a presentation from workers members on potential repercussions from the failure of Silicon Valley Financial institution and different tumult within the monetary sector that started in early March.
Although Vice Chair for Supervision Michael Barr mentioned the banking sector “is sound and resilient,” workers economists mentioned the economic system will take a success.
“Given their evaluation of the potential financial results of the latest banking-sector developments, the workers’s projection on the time of the March assembly included a light recession beginning later this 12 months, with a restoration over the next two years,” the assembly abstract mentioned.
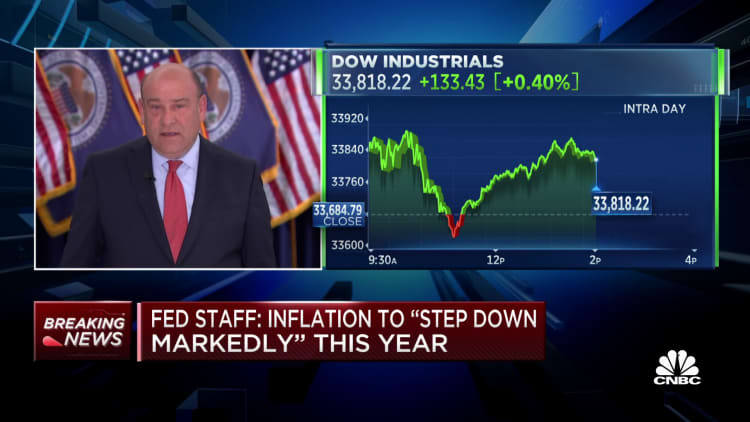
Projections following the assembly indicated that Fed officers anticipate gross home product development of simply 0.4% for all of 2023. With the Atlanta Fed monitoring a first-quarter achieve round 2.2%, that might point out a pullback later within the 12 months.
That disaster had prompted some hypothesis that the Fed may maintain the road on charges, however officers confused that extra wanted to be accomplished to tame inflation.
FOMC officers finally voted to extend the benchmark borrowing charge by 0.25 proportion level, the ninth enhance over the previous 12 months. That introduced the fed funds charge to a goal vary of 4.75%-5%, its highest degree since late 2007.
The speed hike got here lower than two weeks after Silicon Valley Financial institution, on the time the seventeenth largest establishment within the U.S., collapsed following a run on deposits. The failure of SVB and two others spurred the Fed to create emergency lending amenities to verify banks may proceed operations.
For the reason that assembly, inflation knowledge has been principally cooperative with the Fed’s objectives. Officers mentioned on the assembly that they see costs falling additional.
“Reflecting the consequences of much less projected tightness in product and labor markets, core inflation was forecast to gradual sharply subsequent 12 months,” the minutes mentioned.
However concern over broader financial situations remained excessive, notably in gentle of the banking issues. Following the collapse of SVB and the opposite establishments, Fed officers opened a brand new borrowing facility for banks and eased situations for emergency loans on the low cost window.
The minutes famous that the packages helped get the trade via its troubles, however officers mentioned they anticipate lending to tighten and credit score situations to deteriorate.
“Even with the actions, individuals acknowledged that there was important uncertainty as to how these situations would evolve,” the minutes mentioned.
Half-point hike if not for disaster?
A number of policymakers questioned whether or not to carry charges regular as they watched to see how the disaster unfolded. Nevertheless, they relented and agreed to vote for one more charge hike “due to elevated inflation, the power of the latest financial knowledge, and their dedication to convey inflation right down to the Committee’s 2 % longer-run purpose.”
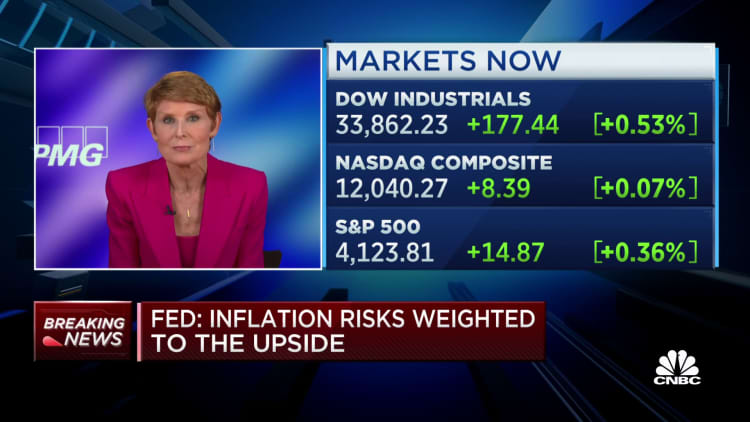
In reality, the minutes famous that some members had been leaning towards a half-point charge rise previous to the banking issues. Officers mentioned inflation is “a lot too excessive” although they confused that incoming knowledge and the impression of the hikes should be thought-about when formulating coverage forward.
“A number of individuals emphasised the necessity to retain flexibility and optionality in figuring out the suitable stance of financial coverage given the extremely unsure financial outlook,” the minutes mentioned.
Inflation knowledge has been usually cooperative with the Fed’s goals.
The private consumption expenditures worth index, which is the inflation gauge policymakers watch probably the most, elevated simply 0.3% in February and was up 4.6% on an annual foundation. The month-to-month achieve was lower than anticipated.
Earlier Wednesday, the buyer worth index confirmed an increase of simply 0.1% in March and decelerated to a 5% annual tempo, the latter determine down a full proportion level from February.
Nevertheless, that headline CPI studying was held again principally by tame meals and power costs, and a lift in shelter prices drove core inflation greater by 0.4% for the month and 5.6% from a 12 months in the past, barely above the place it was in February. The Fed expects housing inflation to gradual via the 12 months.
There was some unhealthy information on the inflation entrance: A month-to-month survey from the New York Fed confirmed that inflation expectations over the following 12 months elevated half a proportion level to 4.75% in March.
Markets as of Wednesday afternoon had been assigning a couple of 72% probability of yet another quarter proportion level charge hike in Could earlier than a coverage pivot the place the Fed cuts earlier than the top of the 12 months, in accordance with CME Group knowledge.
Although the FOMC accredited a rise in March, it did alter language within the post-meeting assertion. The place earlier statements referred to the necessity for “ongoing will increase,” the committee modified the phrasing to point that extra hikes “could also be applicable.”