The Federal Reserve on Wednesday raised its benchmark rate of interest by 1 / 4 proportion level and gave little indication it’s nearing the top of this mountain climbing cycle.
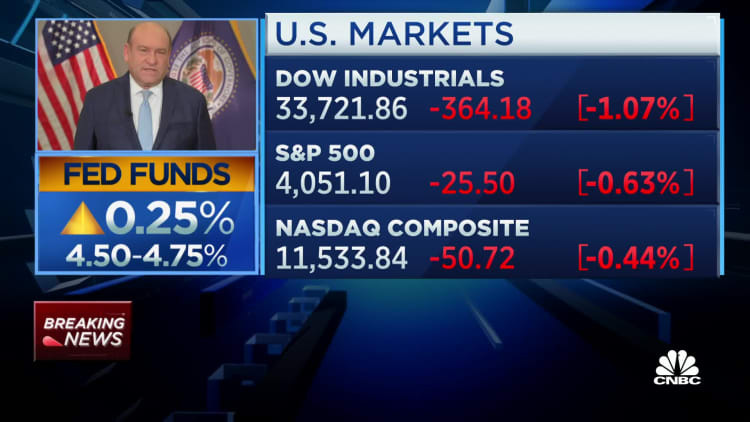
Aligning with market expectations, the rate-setting Federal Open Market Committee boosted the federal funds charge by 0.25 proportion level. That takes it to a goal vary of 4.5%-4.75%, the best since October 2007.
The transfer marked the eighth improve in a course of that started in March 2022. By itself, the funds charge units what banks cost one another for in a single day borrowing, however it additionally spills by way of to many client debt merchandise.
The Fed is concentrating on the hikes to deliver down inflation that, regardless of current indicators of slowing, remains to be working close to its highest stage for the reason that early Nineteen Eighties.
The post-meeting assertion famous that inflation “has eased considerably however stays elevated,” a tweak on earlier language.
“Inflation information obtained over the previous three months present a welcome discount within the month-to-month tempo of will increase,” Fed Chairman Jerome Powell mentioned in his post-meeting information convention. “And whereas current developments are encouraging, we’ll want considerably extra proof to be assured that inflation is on a sustained downward path.”
Markets, nevertheless, had been seeking to this week’s assembly for indicators that the Fed could be ending the speed will increase quickly. However the assertion offered no such indicators. At first, shares fell within the wake of the announcement, with the Dow Jones Industrial Common tumbling greater than 300 factors.
Nonetheless, the market rebounded throughout Powell’s press convention, after he acknowledged that “the disinflationary course of” had began. Main averages in the end turned optimistic as market commentary centered on Powell’s considerably optimistic feedback on progress towards inflation.
“We are able to now say I feel for the primary time that the disinflationary course of has began,” Powell mentioned, whereas additionally noting that it will be “very untimely to declare victory or to suppose we actually bought this.”
The Fed’s assertion included language noting that the FOMC nonetheless sees the necessity for “ongoing will increase within the goal vary.” Market members had been hoping for some softening of the phrase, however the assertion, accepted unanimously, stored it intact.
The assertion altered one half when describing what is going to decide the long run coverage path.
Officers mentioned they’d decide the “extent” of future charge will increase primarily based on components comparable to the results to date of the speed hikes, the lags during which coverage has an impression, and developments in monetary circumstances and the financial system. Beforehand, the assertion mentioned it will use these components to find out the “tempo” of future hikes, a doable nod that the committee sees an finish to the will increase someplace, or at the least a continuation of smaller strikes forward.
In 2022, the Fed accepted 4 consecutive 0.75 proportion level strikes earlier than going to a smaller 0.5 proportion level improve in December. In current public statements, a number of officers mentioned they suppose the central financial institution at the least can reduce on the scale of the hikes, with out signaling once they may finish.
Whereas it was elevating its benchmark charge, the committee characterised financial development as “modest” although it famous solely that unemployment “has remained low.” The most recent job market evaluation omitted earlier language that employment positive factors have been “strong.”
In any other case, the assertion remained intact from earlier messages because the Fed continues its efforts to arrest inflation.
Fed firmly centered on inflation
Fed coverage is assumed to work on a lag – when the central financial institution raises charges, it takes time for the financial system to regulate to tighter controls on cash.
This explicit spherical of inflation began resulting from Covid-related components comparable to clogged provide chains and surging demand for items over companies. The warfare in Ukraine aggravated rising gasoline costs, whereas unprecedented fiscal and financial stimulus fueled growing prices throughout quite a lot of items and companies.
Meals costs have risen greater than 10% over the previous 12 months. Egg costs alone have soared 60%, butter is up greater than 31% and lettuce has jumped 25%, in accordance with Labor Division information by way of December. Fuel costs had been ticking decrease towards the top of 2022 however have popped greater in current days, hitting $3.50 a gallon nationally for a rise of about 30 cents over the previous month, in accordance with AAA.
Fed officers have remained resolute about tackling inflation, although they’ve mentioned current numbers present pressures might be easing. The patron worth index declined 0.1% in December on a month-to-month foundation and is up 6.5% from a 12 months in the past – down from the height of 9% final summer time however nonetheless properly above the place the Fed feels snug.
Fed’s bond shopping for
Together with the speed hikes, the Fed has been lowering the holdings in its bond portfolio. That has resulted in a discount of about $445 billion since June, because the Fed has focused a capped stage of $95 billion in maturing bonds it’s permitting to roll off every month quite than reinvest.
The stability sheet discount has been the equal of about 2 proportion factors of further charge hikes, in accordance with the San Francisco Fed. The stability sheet remains to be at greater than $8.4 trillion.
Markets are anticipating the place the Fed will lastly finish the will increase.
On the December FOMC assembly, committee members indicated they see the “terminal charge,” or level the place the Fed thinks coverage is sufficiently restrictive, as 5.1%. Markets are betting that quantity is nearer to 4.75%, and so they count on the Fed to begin reducing charges later this 12 months, after yet one more quarter-point improve in March.
Responding to a query from CNBC’s Steve Liesman, Powell mentioned it is “doable” that the funds charge may keep decrease than 5%. However he additionally mentioned it is unlikely the Fed would minimize charges this 12 months until inflation comes down extra quickly.


