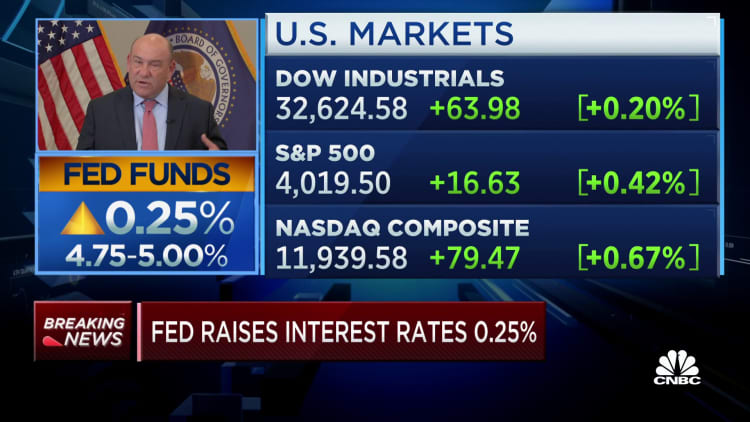
WASHINGTON — The Federal Reserve on Wednesday enacted 1 / 4 proportion level rate of interest improve, expressing warning concerning the current banking disaster and indicating that hikes are nearing an finish.
Together with its ninth hike since March 2022, the rate-setting Federal Open Market Committee famous that future will increase will not be assured and can rely largely on incoming information.
“The Committee will carefully monitor incoming info and assess the implications for financial coverage,” the FOMC’s post-meeting assertion mentioned. “The Committee anticipates that some extra coverage firming could also be acceptable to be able to attain a stance of financial coverage that’s sufficiently restrictive to return inflation to 2 % over time.”
That wording is a departure from earlier statements which indicated “ongoing will increase” can be acceptable to convey down inflation.
Whereas feedback Fed Chair Jerome Powell made throughout a information convention had been taken to imply that the central financial institution could also be nearing the tip of its rate-hiking cycle, he certified that the inflation struggle is not over.
“The method of getting inflation again all the way down to 2% has a protracted strategy to go and is more likely to be bumpy,” the central financial institution chief mentioned.
Additionally, Powell acknowledged that the current occasions within the banking system had been more likely to end in tighter credit score situations, and that was probably why the central financial institution’s tone had softened.
Nonetheless, he mentioned that regardless of market pricing on the contrary, “fee cuts will not be in our base case” for the rest of 2023.
Shares initially rose after the Fed’s choice, however slumped following Powell’s remarks.
“The U.S. banking system is sound and resilient,” the committee mentioned, in its ready assertion. “Latest developments are more likely to end in tighter credit score situations for households and companies and to weigh on financial exercise, hiring, and inflation. The extent of those results is unsure. The Committee stays extremely attentive to inflation dangers.”
In the course of the information convention, Powell mentioned the FOMC thought of a pause in fee hikes in gentle of the banking disaster, however in the end unanimously accredited the choice to lift charges as a consequence of intermediate information on inflation and the energy of the labor market.
“We’re dedicated to restoring value stability and the entire proof says that the general public has confidence that we are going to achieve this, that may convey inflation all the way down to 2% over time. It will be significant that we maintain that confidence with our actions, in addition to our phrases,” Powell mentioned.

The rise takes the benchmark federal funds fee to a goal vary between 4.75%-5%. The speed units what banks cost one another for in a single day lending however feeds by means of to a mess of client debt like mortgages, auto loans and bank cards.
Projections launched together with the speed choice level to a peak fee of 5.1%, unchanged from the final estimate in December and indicative {that a} majority of officers anticipate just one extra fee hike forward.
Knowledge launched together with the assertion exhibits that seven of the 18 Fed officers who submitted estimates for the “dot plot” see charges going greater than the 5.1% “terminal fee.”
The following two years’ value of projections additionally confirmed appreciable disagreement amongst members, mirrored in a large dispersion among the many “dots.” Nonetheless, the median of the estimates factors to a 0.8 proportion level discount in charges in 2024 and 1.2 proportion factors value of cuts in 2025.
The assertion eradicated all references to the impression of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Markets had been carefully watching the choice, which got here with a better diploma of uncertainty than is typical for Fed strikes.
Jerome Powell, chairman of the US Federal Reserve, speaks throughout a information convention following a Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assembly in Washington, DC, on Wednesday, March 22, 2023.
Al Drago | Bloomberg | Getty Pictures
Earlier this month, Powell had indicated the central financial institution might must take a extra aggressive path to tame inflation. However a fast-moving banking disaster thwarted any notion of a extra hawkish transfer – and contributed to normal market sentiment that the Fed shall be slicing charges earlier than the yr involves an in depth.
Estimates launched Wednesday of the place Federal Open Market Committee members see charges, inflation, unemployment and gross home product underscored the uncertainty for the coverage path.
Officers additionally tweaked their financial projections. They barely elevated their expectations for inflation, with a 3.3% fee pegged for this yr, in contrast with 3.1% in December. Unemployment was lowered a notch to 4.5%, whereas the outlook for GDP nudged all the way down to 0.4%.
The estimates for the subsequent two years had been little modified, besides the GDP projection for 2024 got here all the way down to 1.2% from 1.6% in December.
The forecasts come amid a risky backdrop.
Regardless of the banking turmoil and risky expectations round financial coverage, markets have held their floor. The Dow Jones Industrial Common is up some 2% over the previous week, although the 10-year Treasury yield has risen about 20 foundation factors, or 0.2 proportion factors, throughout the identical interval.
Whereas late 2022 information had pointed to some softening in inflation, current stories have been much less encouraging.
The non-public consumption expenditures value index, a favourite inflation gauge for the Fed, rose 0.6% in January and was up 5.4% from a yr in the past – 4.7% when stripping out meals and vitality. That is effectively above the central financial institution’s 2% goal, and the information prompted Powell on March 7 to warn that rates of interest probably would rise greater than anticipated.
However the banking points have difficult the decision-making calculus because the Fed’s tempo of tightening has contributed to liquidity issues.
Closures of Silicon Valley Financial institution and Signature Financial institution, and capital points at Credit score Suisse and First Republic, have raised issues concerning the state of the business.
Whereas large banks are thought of effectively capitalized, smaller establishments have confronted liquidity crunches because of the quickly rising rates of interest which have made in any other case secure long-term investments lose worth. Silicon Valley, for example, needed to promote bonds at a loss, triggering a disaster of confidence.
The Fed and different regulators stepped in with emergency measures that appear to have stemmed quick funding issues, however worries linger over how deep the harm is amongst regional banks.
On the identical, recession issues persist as the speed will increase work their method by means of the financial plumbing.
An indicator that the New York Fed produces utilizing the unfold between 3-month and 10-year Treasurys put the possibility of a contraction within the subsequent 12 months at about 55% as of the tip of February. The yield curve inversion has elevated since then.
Nevertheless, the Atlanta Fed’s GDP tracker places first-quarter progress at 3.2%. Shoppers proceed to spend – although bank card utilization is on the rise – and unemployment was at 3.6% whereas payroll progress has been brisk.


