Fermented meals have grown in recognition and are extensively consumed, partly as a consequence of claims relating to their optimistic impact on digestive well being. Nevertheless, these claims lack adequate scientific help, particularly for lacto-fermented greens.
A workforce of College of Minnesota researchers got down to check these claims, by learning if frequent consumption of lacto-fermented greens, akin to kimchi or kraut, had any impact on the trillions of micro organism that make up the intestine microbiome.
Their findings have been lately printed within the journal Intestine Microbiome.
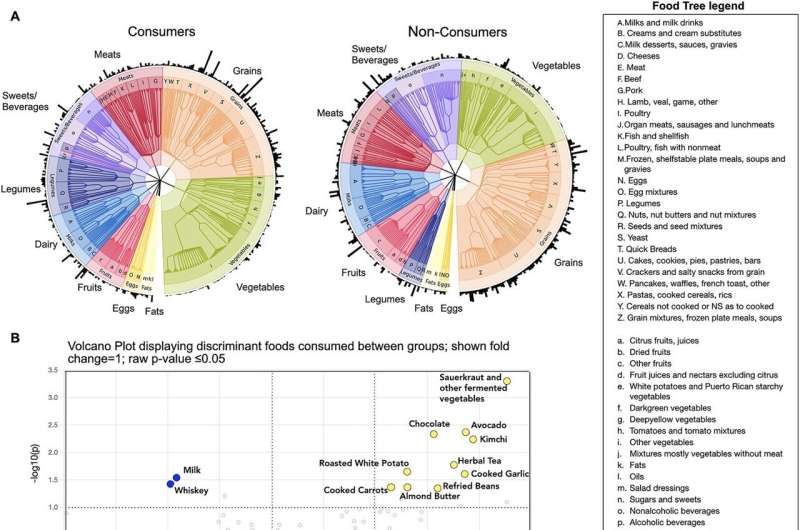
To conduct their research, the researchers collected fecal samples of 23 individuals within the Twin Cities who often consumed at the very least one serving of plant-based fermented meals, 5 instances every week for 2 years. This didn’t embody dairy ferments. Their fecal microbiomes have been studied and in comparison with these of 24 individuals who by no means or not often consumed lacto-fermented greens or different fermented meals, and had not carried out so within the final two years.
The researchers performed an intensive dietary examination of the individuals earlier than starting the experiment and located each customers of lacto-fermented meals and non-consumers began from the same place when it comes to general weight loss plan high quality. They decided the Wholesome Consuming Index rating, a USDA measure of dietary well being, and located each teams have been near the nationwide common rating for adults, which is 58 out of 100. Lacto-fermented vegetable customers have been barely greater at 59 out of 100, and non-consumer had a barely decrease rating of 55 out of 100.
The researchers discovered:
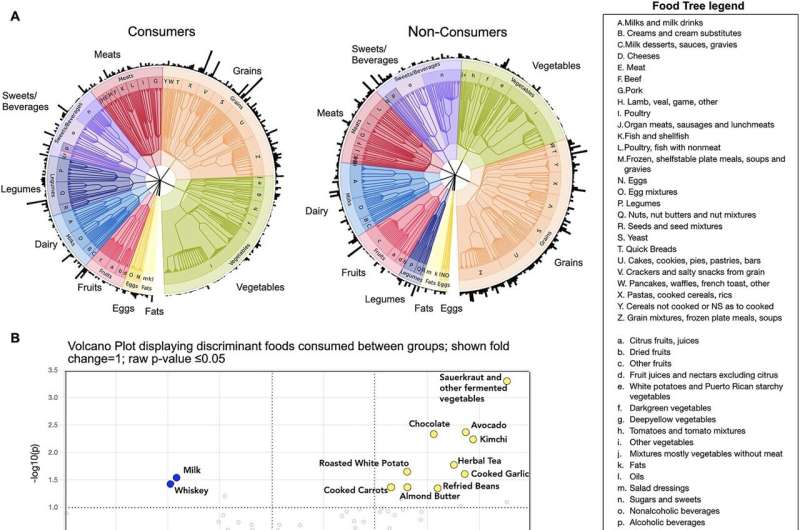
- Probably probiotic micro organism and fungi probably derived from the lacto-fermented greens have been discovered within the feces of some people frequently consuming fermented meals.
- Common consumption of lacto-fermented greens could stimulate micro organism with the potential to supply butyrate, a compound within the intestine that’s extensively identified for its optimistic results on well being.
Lacto-fermented greens have a considerably higher impact on among the capabilities carried out by microorganisms within the intestine and on the vitamins that our microbiome makes use of to carry out capabilities with probably key results on well being. That is demonstrated by the remark that common customers confirmed a higher range of fecal metabolites (small intestine vitamins) and higher manufacturing of microbial vitamins with identified optimistic results on well being akin to acetate and propionate (quick chain fatty acids).
“Our findings help present analysis exhibiting that fermented meals, on this case, lacto-fermented greens, profit the intestine microbiome and metabolome in individuals consuming a typical Western weight loss plan,” mentioned lead creator Kylene Guse, a postdoctoral researcher on the College of South Dakota, previously with the U of M.
Nevertheless, these microbiome-mediated advantages ought to be examined by taking repeated snapshots of an individual’s microbiome over time, and assessing if consumption can enhance particular well being points in people.
“Our findings have implications for well being prevention methods primarily based on the therapeutic energy of wholesome meals,” mentioned Andres Gomez, an assistant professor within the Division of Animal Science. “Sooner or later, we have to check a possible optimistic impact of consuming lacto-fermented greens in topics with particular ailments with a identified microbiome connection, akin to most cancers, weight problems or autoimmune illness, amongst others.”
The workforce is at present assessing how they’ll broaden neighborhood well being and science literacy on the potential advantages of consuming fermented greens and the way the intestine microbiome is a crucial part for well being upkeep. They’re additionally testing the impact of consuming different fermented meals—particularly kombucha—in addressing psychological well being points, as associations emerge between intestine microbes and mind operate
Extra info:
Kylene Guse et al, Common consumption of lacto-fermented greens has higher results on the intestine metabolome in contrast with the microbiome, Intestine Microbiome (2023). DOI: 10.1017/gmb.2023.9
College of Minnesota
Quotation:
Fermented greens discovered to positively influence intestine well being (2023, July 24)
retrieved 24 July 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-07-fermented-vegetables-positively-impact-gut.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.