The subsequent frontier of steady well being monitoring might be pores and skin deep.
Biomedical engineers on the College of Cincinnati say interstitial fluid, the watery fluid discovered between and round cells, tissues or organs within the physique, might present a superb medium for early illness analysis or long-term well being monitoring.
In a paper printed within the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering, they outlined the potential benefits and technological challenges of utilizing interstitial fluid.
“Why we see it as a invaluable diagnostic fluid is steady entry. With blood, you possibly can’t simply take steady readings,” mentioned UC doctoral graduate Mark Friedel, co-lead creator of the research.
“Are you able to think about going about your day with a needle caught in your vein all day? So we want different instruments.”
Researchers are in search of alternate options to observe an individual’s well being and wellness. Sweat is an efficient medium for measuring sure issues like stress or nervousness as a result of it comprises hormones akin to cortisol. However the physique is stingy with different chemical substances that aren’t so simply launched in sweat, Friedel mentioned.
“Sweat glands are massive filters that do not enable all the things to go by means of,” he mentioned. “So greater than half of the issues we need to monitor haven’t any entry to sweat in any respect.”
Blood is the gold normal for well being monitoring. However folks even have liters of interstitial fluid that make up as a lot as 15% of their physique weight.
“The important thing characteristic of blood that makes it so advantageous is we perceive blood rather well,” Friedel mentioned. “In case you have one thing in your blood, we all know what’s going to occur to your coronary heart or your liver,” he mentioned.
Researchers mentioned interstitial fluid comprises most of the identical chemical substances in the identical proportions as blood, providing a possible various to expensive and time-consuming lab work.
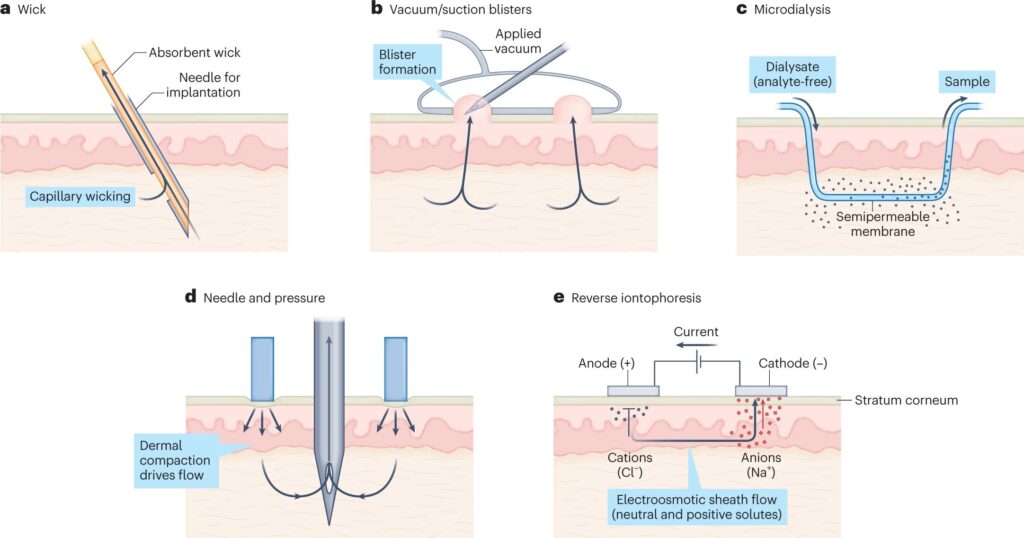
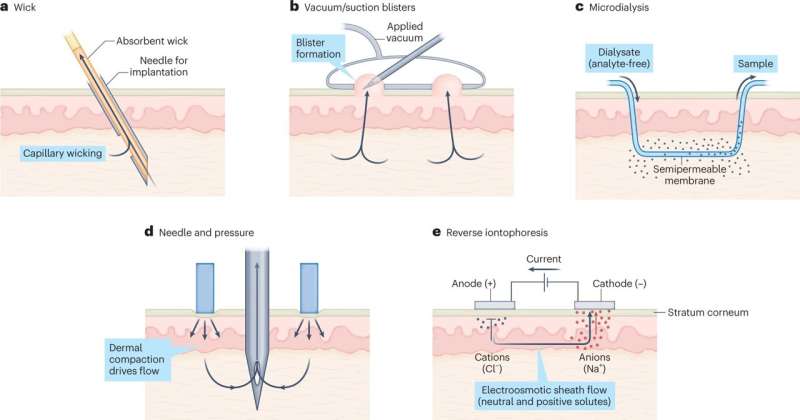
The research outlined the varied methods docs can pattern interstitial fluid, from making use of suction to the pores and skin to deploying microdialysis.
“As biomedical engineers, one in every of our biggest objectives is to assist folks higher handle their well being by making diagnostics extra accessible,” mentioned co-lead creator Ian Thompson at Stanford College.
“A giant barrier to this accessibility is that the majority present diagnostics depend on blood sampling, which might be painful and requires skilled personnel to carry out. Thus, in recent times there was rising curiosity in utilizing interstitial fluid slightly below the pores and skin as a diagnostic pattern that’s extra accessible and fewer painful to extract.”
In UC School of Engineering and Utilized Science professor Jason Heikenfeld’s Novel Units Lab, college students are creating sensors to measure hormones and different chemical substances in interstitial fluid. They use microneedles lower than 1 millimeter in size that pierce the pores and skin by means of a tiny patch.
“Should you had a splinter, it most likely went deeper into your pores and skin than our microneedles,” Friedel mentioned. “They’re typically painless. I do not really feel it more often than not. Essentially the most uncomfortable half is eradicating the tape that holds the gadget down.”
However even when you do not know it is there, your physique does, Friedel mentioned. And this minute response can have an effect on the take a look at outcomes.
“There is a Schrödinger’s observer impact with interstitial fluid. Any time you attempt to accumulate and measure it, you inherently change the fluid itself,” Friedel mentioned. “Should you stick a needle in your pores and skin, your physique turns into infected after which your [sample] ranges change. For steady biomonitoring, we need to know these concentrations as they’re while you’re not being poked with a tiny needle.
“That is why it is such a difficult fluid that hasn’t been used outdoors of diabetes monitoring.”
Nonetheless, researchers say, interstitial fluid holds huge promise for monitoring well being by means of wearable expertise. This might assist docs observe the efficacy of medication to make sure correct dosage or present early analysis of sickness by monitoring the immune system.
However Friedel mentioned there may be nonetheless lots to be taught.
“We’re attempting to unlock the field and browse the directions inside to know what’s in interstitial fluid and what the potentials are for exploiting it,” he mentioned.
Extra data:
Mark Friedel et al, Alternatives and challenges within the diagnostic utility of dermal interstitial fluid, Nature Biomedical Engineering (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41551-022-00998-9
College of Cincinnati
Quotation:
Getting underneath your pores and skin for higher well being with interstitial fluid testing (2023, January 20)
retrieved 20 January 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-01-skin-health-interstitial-fluid.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.