Local weather change isn’t solely inflicting irreversible harm to the inexperienced cowl, they’re equally impacting marine life. A brand new examine appears to counsel that greater than one-fifth of the worldwide ocean has significantly darkened within the final 20 years. This alarming state of the oceans has been dropped at mild by the examine, Darkening of the World Ocean, performed by researchers from College of Plymouth.
The examine by Dr Thomas Davies, Professor Tim Smyth, and crew, counsel that ocean darkening at this scale isn’t solely the most recent ecological disaster, however one which comes with grave implications for marine life and general planetary well being.
What’s ocean darkening?
Darkening of the ocean is basically shrinking of the photic zones or these layers of water the place daylight can go and induce the method of photosynthesis which is vital to all organic processes. The photic layers can go right down to about 200 meters and so they additionally act as a base for almost 90 per cent of the world’s marine life. This layer is liable for rising the productiveness of the ocean which additionally entails regulating local weather and even supporting world fisheries or associated actions.
As a part of the examine, Davies and Smyth used satellite tv for pc knowledge together with refined modelling strategies to analyse adjustments in how the oceans have absorbed mild within the final 20 years. The duo tracked the adjustments utilizing the diffuse attenuation coefficient (Kd 490), a measure of how quickly mild fades because it passes by way of seawater.
The discovering of the examine is essential because it signifies that between 2003 and 2022, almost 21 per cent of the worldwide ocean skilled darkening. Whereas 9 per cent (equal to the world of the continent of Africa) noticed a decline in photic zone depth larger than 50 metres, 2.6 per cent noticed discount of over 100 metres.

Combined world image
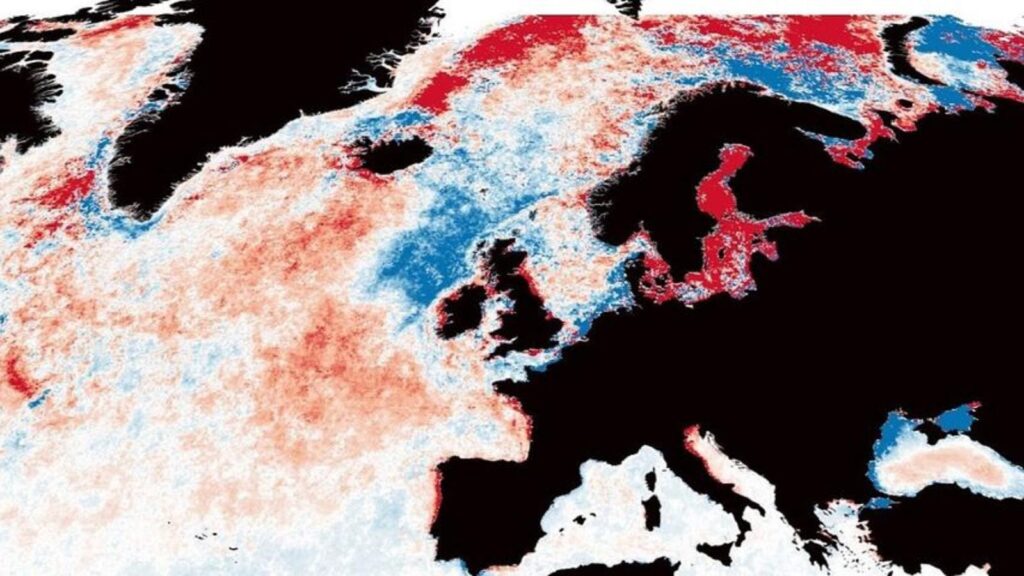
Regardless that the examine states huge lack of mild, across the similar two decade-span, a substantial a part of the worldwide ocean has truly turn into lighter. This reveals that the predictability of ocean darkening isn’t even throughout all waterways. The North Sea, the japanese UK shoreline, and the Arctic have misplaced extra mild than some other areas, whereas there have even been small areas (e.g. areas of the English Channel) which have had extra mild. These patterns are the results of various environmental situations in numerous areas which incorporates different rainfall, land use, and ocean currents.
Nevertheless, probably the most distinguished darkening was noticed within the open ocean, significantly in climate-sensitive zones just like the Arctic, Antarctic, and Gulf Stream area. Coastal areas just like the Baltic Sea have additionally misplaced photic depth due to erosion of sediments and vitamins from lands.
Story continues under this advert
Why is that this taking place?
In coastal zones, darkening is normally as a consequence of increased runoff of agricultural vitamins, natural matter, and sediments into the ocean with rain which instantly promotes algal blooms that block mild. Within the open ocean, the doubtless causes are adjustments in plankton dynamics, enhance in sea floor temperature and adjustments in ocean circulation.
“There was analysis displaying how the floor of the ocean has modified color during the last 20 years, doubtlessly on account of adjustments in plankton communities. However our outcomes present proof that such adjustments trigger widespread darkening that reduces the quantity of ocean obtainable for animals that depend on the solar and the moon for his or her survival and copy,” Davies defined.
“We additionally depend on the ocean and its photic zones for the air we breathe, the fish we eat, our capability to struggle local weather change, and for the overall well being and wellbeing of the planet. Taking all of that under consideration, our findings signify real trigger for concern”, he added.
Story continues under this advert
Marine life within the shadows
The contraction of photic zones might result in basic shifts in marine ecosystems. These species that use daylight and moonlight cues to feed, transfer, conceal, and reproduce shall be competing for shallower zones. This may upset marine meals webs which are already working exhausting towards an ecosystem with minimal fishing exercise.
Smyth, who’s the pinnacle of Science for Marine Biogeochemistry and Observations on the Plymouth Marine Laboratory, highlighted the ecological hazard. “The ocean is way extra dynamic than it’s usually given credit score for. For instance, we all know the sunshine ranges throughout the water column differ massively over any 24-hour interval, and animals whose behaviour is instantly influenced by mild are much more delicate to its processes and alter. If the photic zone is lowering by round 50 m in giant swathes of the ocean, animals that want mild shall be pressured nearer to the floor the place they must compete for meals and the opposite sources they want. That would result in basic adjustments in the whole marine ecosystem,” Smyth stated.
The indicator species used on this experiment was Calanus copepods, a extremely photosensitive zooplankton. These animals are on the middle of the marine meals chain and use very faint mild cues from the Solar and Moon for vertical migrations throughout the day and numerous different behaviours.
Story continues under this advert
Underwater habitat disaster
The examine infers ocean darkening as possibly one of many greatest world habitat loss instances ever in latest reminiscence. Animals relying on mild are being constrained to slender vertical areas, rising predation and larger competitors for sources. In the end, this may increasingly kill biodiversity, disrupt oceanic carbon biking, oxygen manufacturing, and ocean buffering towards local weather change.
(This text has been curated by Prachi Mishra, who’s an intern with The Indian Specific)