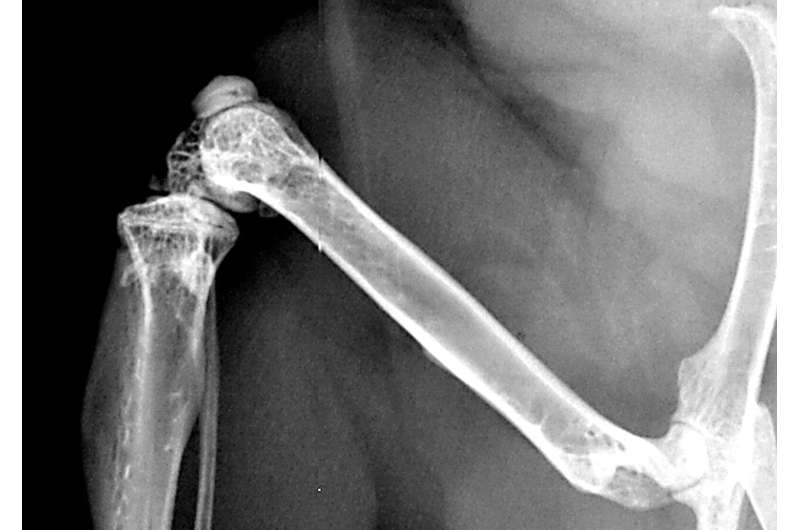
A research at Ulm College and its Medical Heart has uncovered the molecular mechanisms by which psychological trauma and different massively anxious experiences decelerate the therapeutic of bone fractures.
The analysis crew, which included scientists from Canada and Japan, was in a position to reveal that sure immune cells reply to stress by producing an enzyme, which in flip promotes the discharge of stress hormones. These stress hormones act domestically on the bone the place they inhibit the conversion of cartilage cells into bone cells, thus slowing down bone development and fracture therapeutic.
Emergency rescue employees expertise huge stress, as do victims of pure disasters and acts of violence. Within the occasion of a critical harm, this doesn’t stay with out penalties. It’s already recognized that massively anxious and traumatic experiences decelerate wound and bone therapeutic.
Researchers on the College Medical Heart Ulm have now uncovered the molecular mechanism underlying the damaging results of stress on bone metabolism and regeneration.
“A continued excessive psychological stress load causes sure immune cells to provide an enzyme, which in flip triggers the manufacturing and launch of stress hormones that compromise bone development,” mentioned Professor Stefan Reber summing up their findings. The neurobiologist, who heads the Laboratory for Molecular Psychosomatics on the Division of Psychosomatic Drugs and Psychotherapy in Ulm, coordinated the research along with Professor Melanie Haffner-Luntzer from the Institute of Orthopaedic Analysis and Biomechanics. They printed their work within the journal Nature Communications.
The accountable immune cells are so-called neutrophil granulocytes, which belong to the white blood cells and thus to the non-specific, innate immune system. Extreme psychological stress causes these immune cells to provide the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase (TH). This enzyme then triggers the native manufacturing and launch of sure stress hormones (catecholamines) within the fracture hematoma. Adrenaline is included within the group of catecholamines, as are its precursors noradrenaline and dopamine. These domestically secreted stress hormones act on the areas the place new bone materials ought to be rising. To be able to kind new bone, cartilage cells are transformed into bone cells.
“The impact of those stress hormones impairs this cartilage-to-bone transition, slowing down bone development and fracture therapeutic,” explains Dr. Miriam Tschaffon-Müller. The scientist from the Institute of Orthopaedic Analysis and Biomechanics is without doubt one of the two first authors of the research, along with Elena Kempter, a doctoral researcher at Reber’s lab.
With using cell-type-specific knockout mice with suppressed TH expression and blocked adrenoceptors, the scientists have been in a position to reveal this stress-induced mechanism of motion on the molecular genetic degree. The knockout mice confirmed no stress-induced inhibition of bone therapeutic. Within the medical a part of the research, the researchers collaborated with the Division of Orthopaedic Trauma-, Hand-, Plastic- and Reconstruction Surgical procedure and the Division of Psychosomatic Drugs and Psychotherapy to look at sufferers with ankle fractures.
“The results of the medical research confirmed: when the psychological pressure brought on by stress, trauma or melancholy was thought of excessive, sufferers additionally have been characterised by excessive ranges of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) within the fracture hematoma, and hampered fracture therapeutic,” says Haffner-Luntzer. What is especially astounding: the decisive issue for these measurable results was the sufferers’ subjective score of the psychological stress load in addition to their ache notion.
The research’s findings might need implications for medical apply, giving it instant relevance. For instance, it may be advisable to contemplate the sufferers’ stress or trauma historical past when treating fractures and different huge accidents. Below sure circumstances, it’d make sense to make use of beta blockers to dampen the damaging affect of stress hormones on bone therapeutic.
Extra info:
Miriam E. A. Tschaffon-Müller et al, Neutrophil-derived catecholamines mediate damaging stress results on bone, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-38616-0
Supplied by
Universität Ulm
Quotation:
Continual stress is unhealthy for damaged bones: How psychological stress impairs bone development and fracture therapeutic (2023, July 13)
retrieved 13 July 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-07-chronic-stress-bad-broken-bones.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.