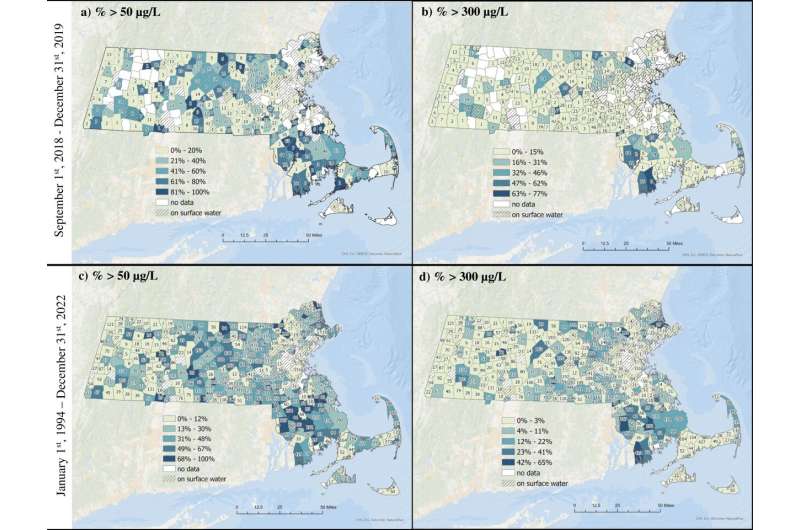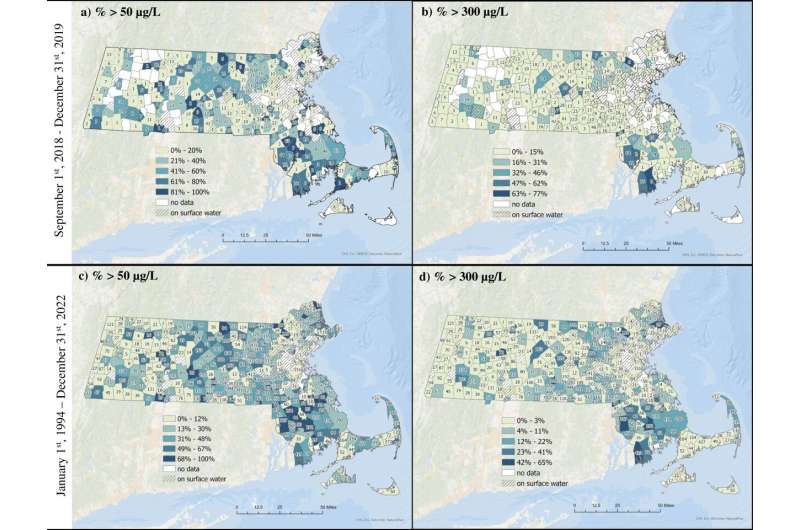
Manganese is an unregulated contaminant typically present in consuming water, however secure ranges of this metallic are at present unknown, and prior analysis has indicated that overexposure to manganese could also be dangerous to kids.
Now, a examine led by researchers at Boston College Faculty of Public Well being (BUSPH) has discovered that concentrations of manganese in a Massachusetts neighborhood’s consuming water typically surpassed the utmost advisable ranges of manganese acknowledged in present pointers.
Revealed within the Journal of Publicity Science & Environmental Epidemiology, the findings additionally counsel that the noticed manganese ranges could also be excessive sufficient to pose a threat to kids and different weak communities who’re uncovered.
Manganese is a naturally occurring part of soil and rock, and it’s each an important nutrient and a poisonous substance—so, too little or an excessive amount of publicity will be dangerous to well being. Even if manganese is discovered in lots of communities’ consuming water throughout the US, it isn’t federally regulated. The US Environmental Safety Company has developed pointers that establish a most degree of day by day publicity to manganese for “aesthetic” functions (i.e. colour and style), in addition to for the general well being and security of the final inhabitants. However these pointers are solely suggestions; they can’t be enforced in the best way that established main requirements can.
“Some degree of manganese is required for well being, however rising proof means that extra ranges of manganese can hurt kids’s brains,” says examine lead and corresponding writer Alexa Friedman, a doctoral pupil at BUSPH on the time of the examine. “Our findings counsel that the extent of manganese that’s current in public consuming water exceeded, on common, the aesthetic pointers 40% of the time, and health-based pointers 9% of the time. These information help the necessity for a legally enforceable main consuming water commonplace for manganese as a way to higher defend kids’s well being.”
The brand new examine is among the many first to look at manganese concentrations in consuming water throughout time and placement in america.
For the examine, Friedman and colleagues examined residential faucet water samples collected between September 2018 to December 2019 within the suburban neighborhood of Holliston, Mass., as a part of a community-initiated pilot examine referred to as ACHIEVE (Assessing Youngsters’s Environmental Exposures). Holliston residents had reported considerations in regards to the high quality of their consuming water and the security of kids locally after noticing that their faucet water turned black or brown sometimes. Communities that obtain faucet water from shallow aquifers are particularly weak to being uncovered to excessive ranges of manganese, and Holliston residents depend on this supply for nearly all of their consuming water.
“Though common water manganese concentrations in Holliston had been comparatively low, our work confirmed that ranges nonetheless typically exceed the present aesthetic and health-based pointers,” says examine senior writer Birgit Claus Henn, affiliate professor of environmental well being at BUSPH. “Whereas the prevailing pointers could also be useful benchmarks, with out an enforceable commonplace in place, there’s a restrict to what will probably be carried out to make sure the water is secure to drink and/or meets these pointers.”
The researchers additionally in contrast their community-level manganese samples to public information on state-wide manganese ranges. They discovered comparable ranges, suggesting that overexposure to manganese is just not an remoted problem throughout the Holliston neighborhood.
To raised perceive the well being dangers of publicity to manganese in consuming water, Claus Henn and Friedman advocate that policymakers and different researchers improve monitoring of manganese in water, conduct well being research on this publicity in communities, and contemplate an enforceable commonplace.
“If residents are involved in regards to the degree of manganese of their consuming water, they need to refer to those sources on-line from Massachusetts Division of Environmental Safety,” Friedman says. “It’s also essential to know that manganese can’t be eliminated by boiling the water, and lots of family filters should not efficient for eradicating manganese from water,” she provides. “Residents ought to solely use filters which are able to eradicating manganese, and the filtration models ought to clearly state this functionality.”
Extra info:
Alexa Friedman et al, Manganese in residential consuming water from a community-initiated case examine in Massachusetts, Journal of Publicity Science & Environmental Epidemiology (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41370-023-00563-9
Boston College
Quotation:
Massachusetts consuming water might include unsafe ranges of manganese (2023, July 10)
retrieved 11 July 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-07-massachusetts-unsafe-manganese.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.