(Bloomberg) — The long-simmering concept that the US authorities ought to stand prepared to purchase again Treasury securities from buyers to enhance market functioning is transferring nearer to actuality.
Most Learn from Bloomberg
Whereas the Treasury Division has carried out buybacks previously — most not too long ago between 2000 and 2002 — and whereas its business advisers since then have urged it to think about establishing a program, steps taken in that course final week have been greater than specialists anticipated.
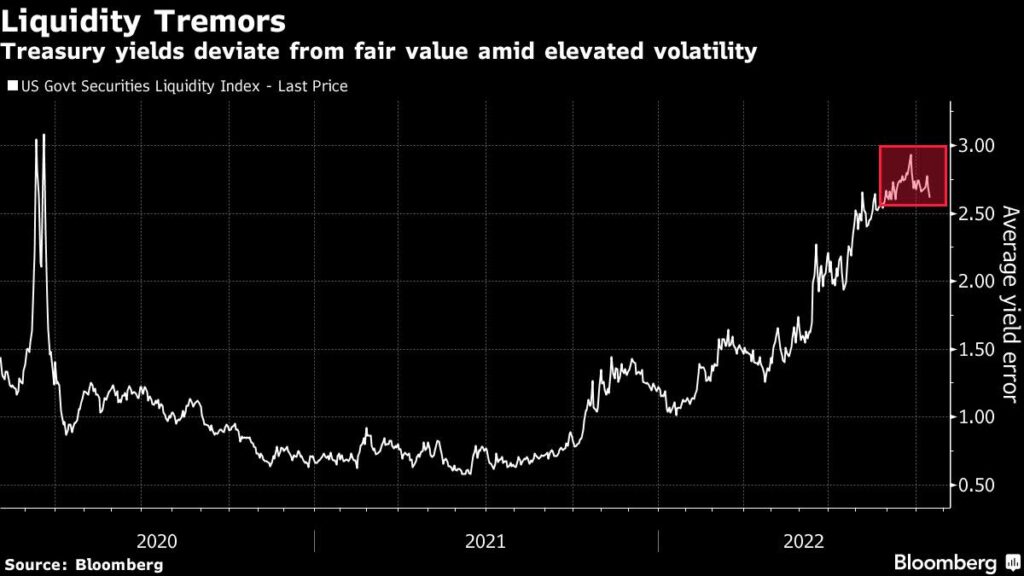
Liquidity metrics for the US authorities debt market are approaching disaster ranges after a 12 months of steep losses for bonds brought on by rising inflation and Federal Reserve interest-rate will increase, and with the central financial institution concurrently chopping a few of its holdings, the scenario might worsen. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen expressed concern about it final week.
“After we warned final week that Treasury buybacks may start to enter the debt administration dialog, we didn’t count on them to leap so abruptly into the limelight,” Wrightson ICAP economist Lou Crandall wrote in a observe to shoppers. “September’s liquidity strains might have sharpened the Treasury’s curiosity in buybacks, however this isn’t only a knee-jerk response to current market developments.”
The precise step taken by the Treasury was in its quarterly survey of major sellers, launched Friday in reference to the financing plan to be introduced Nov. 2. The 25 sellers have been requested for an in depth evaluation of the deserves and limitations of a buyback program for presidency securities. When the final financing plan was launched in August, the division’s business advisers on the Treasury Borrowing Advisory Committee really helpful additional evaluation of the problem.
Excessive Volatility
Taken along with Yellen’s current feedback and excessive volatility within the UK bond market in current weeks, the question suggests “that the November refunding will seemingly present extra progress towards opening a buyback facility,” JPMorgan Chase & Co. charges strategists stated in an Oct. 14 analysis observe. Strategists at Financial institution of America Corp. predicted a rollout in Might 2023.
The buybacks in 2000 to 2002 have been achieved to permit the Treasury to proceed to promote new bonds to keep up its market entry at a time when the federal authorities was working a funds surplus and didn’t want the cash. Funds raised by promoting new bonds have been used to repurchase previous ones.
Beneath present circumstances, which embody giant federal deficits, a buyback program would have completely different functions. They embody including liquidity to components of the market most in want of it, and permitting Treasury payments to be offered in additional constant portions, with proceeds used for buybacks of securities much less in demand.
Enhancing Efficiency
The phase of the market seen to have essentially the most to realize from a buyback program rallied Friday after the survey was launched. Twenty-year bonds, reintroduced in Might 2020 in portions that swamped demand, outperformed neighboring sectors. Crandall stated that’s misguided, and that debt managers with “a restricted amount of money to commit to enhancing the efficiency of the general market” are “not going to pour a disproportionate quantity into salvaging the 20-year sector.”
Treasury liquidity metrics final month reached the worst ranges because the market mayhem on the onset of the pandemic. The Bloomberg US Authorities Securities Liquidity Index — a gauge of deviations in yields from a good worth mannequin — stays close to the best ranges since March 2020, when a flight to money prompted the Fed to start shopping for securities to stabilize the market.
“You possibly can drive a truck via the bid-ask unfold” for some securities, Deborah Cunningham, chief funding officer of worldwide liquidity markets and senior portfolio supervisor at Federated Hermes, stated in a Bloomberg Tv interview Oct. 3.
The extremes of volatility in US Treasuries are including to the strains evident throughout world property, stated Chamath De Silva, a senior portfolio supervisor for Sydney-based BetaShares Holdings, which oversees the equal of $2.7 billion in fastened earnings exchange-traded funds.
“That does have precise implications for liquidity at a market construction degree, and if there’s elevated price volatility sellers have much less capability to warehouse danger throughout authorities bonds in addition to unfold merchandise,” De Silva stated.
Small Starting
Financial institution of America strategists, who’ve been advocating for a buyback program since March 2020, envision an initially small one which received’t aggressively improve benchmark invoice or coupon sizes for funding.
“Treasury debt managers are danger averse, cautious, and deliberate coverage makers,” strategists led by Mark Cabana wrote in a observe. “They rightfully don’t rush choices. Buyback implementation will seemingly be no completely different.”
Not addressed within the survey questions was the chance that buybacks could also be utilized in a restricted manner to assist the Treasury handle the its subsequent encounter with the federal debt ceiling, as Wrightson’s Crandall expects.
A “extra speedy and aggressive” implementation can’t be dominated out, although, if Treasury market functioning breaks down, the Financial institution of America strategists stated.
(Provides remark from fund supervisor in twelfth, thirteenth paragraphs.)
Most Learn from Bloomberg Businessweek
©2022 Bloomberg L.P.