College of Wisconsin–Madison researchers have lately revealed that the effectiveness of frequent antibiotics may rely on the neighborhood the place you reside. Their work is revealed in Scientific Reviews.
Led by postdoctoral fellow Laurel Legenza, researchers at UW–Madison’s College of Pharmacy and State Cartographer’s Workplace labored with colleagues from three Wisconsin well being methods to mix antibiotic resistance knowledge from totally different areas all through the state to gauge the effectiveness of a pair of frequent antibiotic remedies for Escherichia coli infections.
The mix of knowledge allowed the staff to establish neighborhood-level patterns in how properly the antibiotics handled E. coli. They discovered significant variations between census block teams within the pathogen’s susceptibility to the 2 antibiotics. Census block teams are a smaller unit inside census tracts, every dwelling to round 600 to three,000 folks.
The research is an progressive strategy to the longstanding well being care apply of monitoring antibiotic resistance.
“Antibiotic resistance stats usually are not new, however often they’re executed at a well being system degree,” says Legenza. “Some massive well being methods could observe resistance on the ICU degree and evaluate it to the final hospital, however the knowledge will not be properly understood at a group degree. We took all that knowledge and checked out the place these sufferers stay.”
What is the large deal? Mapping variations in antibiotic resistance may assist sufferers obtain higher knowledgeable therapy selections from their well being care suppliers, Legenza says. As an example, resistance maps may reveal neighborhoods the place E. coli infections are simply handled with antibiotics with fewer unwanted side effects.
The research presents a proof-of-concept that such granular resistance mapping is feasible. The analysis staff is already planning extra mapping research and investigations into socio-economic and environmental elements which will play a task in variations.
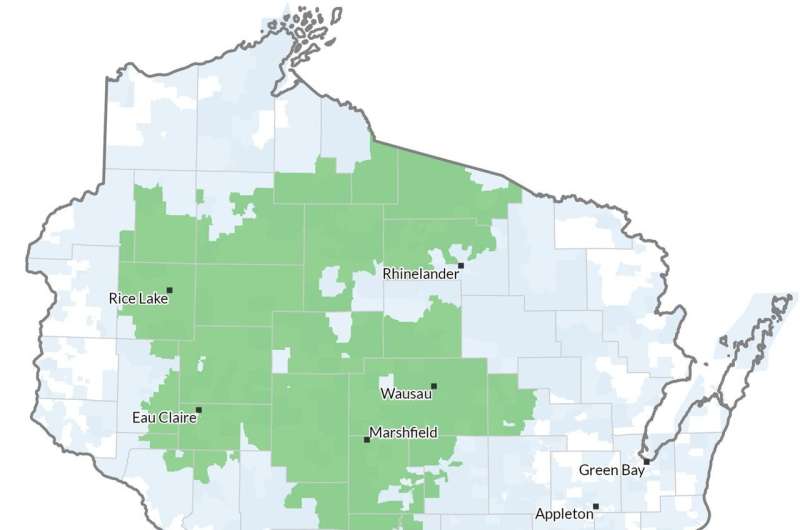
The researchers analyzed knowledge from Wisconsin well being methods representing rural and concrete areas in several elements of the state: Fort HealthCare, Marshfield Clinic Well being System and UW Well being.
Marshfield Clinic spans largely rural stretches of central and northern Wisconsin but additionally serves mid-size cities together with Eau Claire and Wausau, whereas UW Well being encompasses the state’s second largest metro space in Dane County in addition to a number of outlying counties. Fort HealthCare is a smaller, principally rural well being system primarily based in Fort Atkinson, which is about midway between Madison and Milwaukee.
Utilizing strategies that defend affected person confidentiality, the researchers examined 90,000 information from affected person laboratory samples the place E. coli was detected and checked out whether or not every pattern was inclined to or might be handled by frequent antibiotics: ciprofloxacin and a mixture of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim.
They discovered variations within the bacterium’s susceptibility to every therapy inside each city and rural elements of all three well being methods.
“What the information clearly reveals is that resistance patterns are probably totally different in several neighborhoods,” says Legenza.
Additional, Legenza and her colleagues had been in a position to establish particular census tracts as “chilly spots” or “sizzling spots” of susceptibility.
Antimicrobial resistance is a rising public well being risk in america and globally. As sure micro organism and fungi acquire the flexibility to evade medicine designed to deal with them, sufferers face a rising danger of infections which can be tough to deal with. Greater than 2.8 million antimicrobial-resistant infections happen within the U.S. every year, in line with the U.S. Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention, and greater than 35,000 folks die yearly consequently.
Prior analysis has proven geographic variations in antimicrobial resistance, however few research have mapped resistance patterns within the U.S., and none with as a lot granular element as this new report. The neighborhood-level maps construct on a earlier research Legenza led that mapped antibiotic resistance patterns in Wisconsin at a broader degree.
Extra data:
Laurel Legenza et al, A geospatial strategy to establish patterns of antibiotic susceptibility at a neighborhood degree in Wisconsin, United States, Scientific Reviews (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-33895-5
College of Wisconsin-Madison
Quotation:
New maps present antimicrobial resistance varies inside Wisconsin neighborhoods (2023, July 27)
retrieved 28 July 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-07-antimicrobial-resistance-varies-wisconsin-neighborhoods.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.


