Researchers now have a novel useful resource for figuring out new biomarkers of environmental exposures in youth and understanding their well being results. That is because of a examine led by the Barcelona Institute for International Well being (ISGlobal), an establishment supported by la Caixa Basis, which systematically documented all associations between a variety of youth exposures and molecular profiles at totally different ranges, together with the epigenome (DNA methylation), transcriptome (gene expression) and metabolome (metabolites).
The findings, that are a part of the ATHLETE venture, have been revealed in Nature Communications.
Well being relies upon significantly on the atmosphere. Actually, 70 to 90% of the chance of creating a illness is set by the exposome, a large number of environmental elements (i.e., non-genetic elements) to which persons are uncovered all through life. And but, scientists nonetheless have restricted information on these environmental hazards, how they work together, and what organic processes they set off.
“Youth is a very essential interval, since exposures throughout these developmentally susceptible durations might have pronounced results on the molecular stage, which will not be clinically detectable till maturity,” explains Martine Vrijheid, Head of the Childhood and Atmosphere Program at ISGlobal.
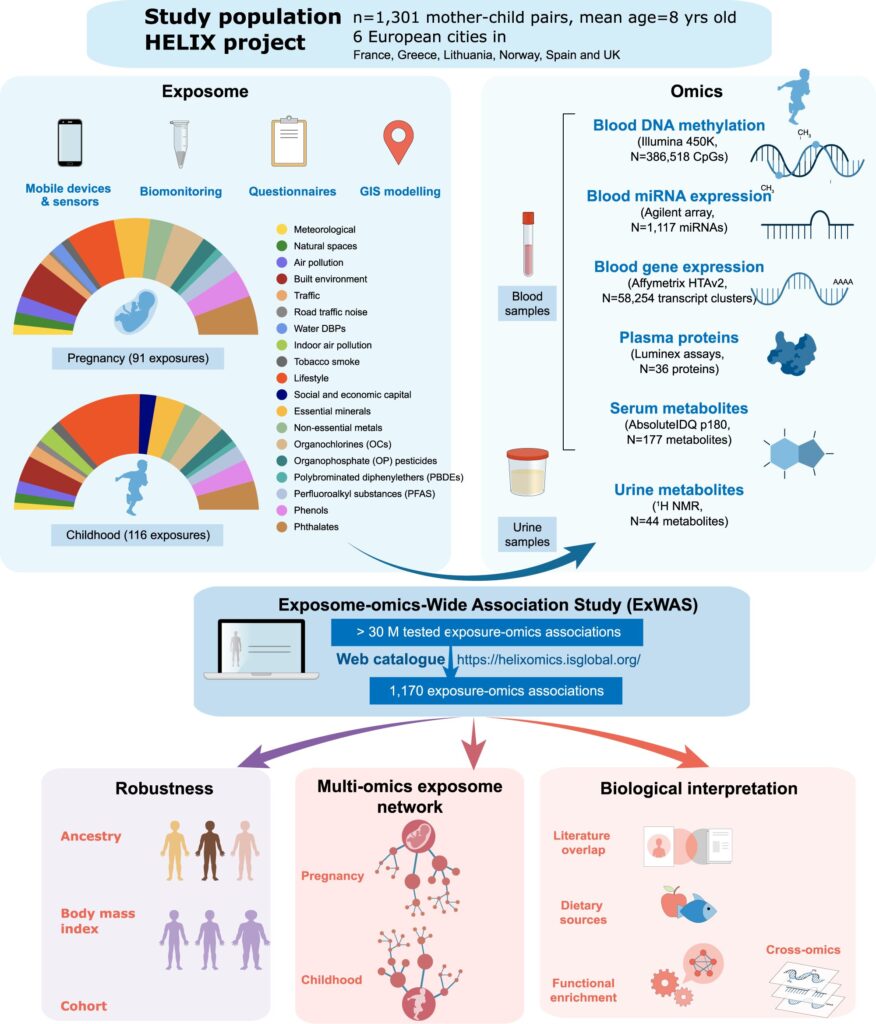
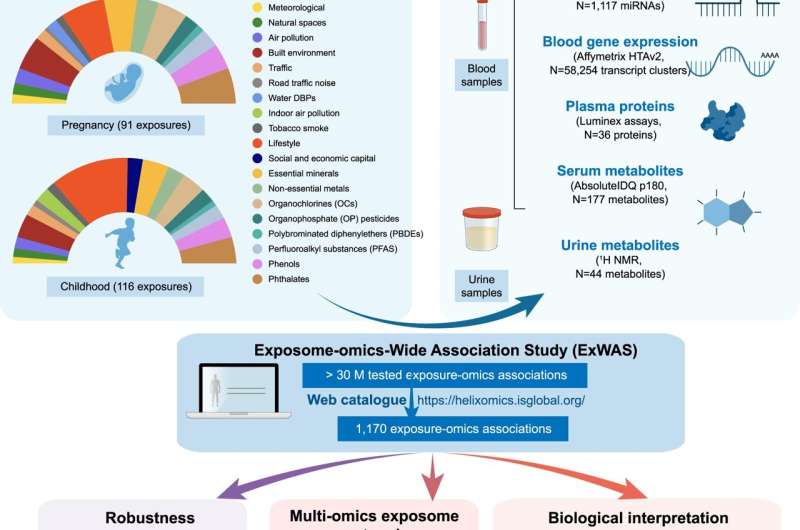
On this examine, the analysis crew led by Vrijheid aimed to affiliate a number of chemical, out of doors, social and way of life exposures (92 in being pregnant and 116 when the kids have been 6 to 11 years previous), with molecular profiles in the identical youngsters (DNA methylation and gene transcription in blood, plasma proteins, and metabolites in serum and urine). The evaluation included 1,301 mother-child pairs of the Human Early Life Exposome (HELIX) venture, a long-term cohort examine in six European international locations (Spain, U.Ok., France, Lithuania, Norway and Greece).
“The high-performance computing, utilizing large parallel computer systems, allowed us to beat one of many predominant challenges confronted in massive ‘omics’ information analyses,” says Juan R Gonzalez, senior co-author. The evaluation recognized 1,170 important associations (249 in being pregnant and 921 in childhood) which give insights into potential organic responses and sources of publicity. Being pregnant exposures, reminiscent of maternal smoking, the heavy metallic cadmium, or the hint mineral molybdenum, have been principally related to adjustments in DNA methylation. In distinction, childhood exposures have been related to signatures in any respect molecular ranges, most significantly with metabolites in serum. The findings revealed, for instance, that youngsters are uncovered to chemical pollution by their food plan.
“We recognized novel multi-omics associations with childhood publicity to important hint parts, climate circumstances, indoor air high quality, and phthalates and parabens,” says Léa Maitre, first writer. “By visualizing these associations as networks, we will higher perceive if a given molecular profile is related to a number of exposures or vice versa, and thereby determine potential organic pathways,” she provides.
Certainly, the findings present believable mechanisms of illness for six teams of exposures: copper, tobacco smoke, indoor air high quality throughout childhood, persistent natural pollution, phthalates and parabens, and climate circumstances. For instance, little one publicity to copper was related to nearly 90 molecular options, together with elevated ranges of C-reactive protein (an irritation marker). Temperature, humidity and different climate circumstances in the course of the month earlier than the samples have been taken, have been related to serum metabolites concerned in sleep and despair, proteins concerned in thermoregulation, and immune response genes.
“With the wealthy exposome and molecular info obtainable in our catalog, we offer a worthwhile useful resource to the scientific group for locating publicity biomarkers, figuring out publicity sources, enhancing the understanding of illness mechanisms, and, finally, selling public well being insurance policies,” concludes Vrijheid.
Léa Maitre et al, Multi-omics signatures of the human youth exposome, Nature Communications (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-34422-2. www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-34422-2
Barcelona Institute for International Well being
Quotation:
New examine supplies a novel useful resource for understanding how environmental exposures in youth have an effect on our well being (2022, November 21)
retrieved 21 November 2022
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2022-11-unique-resource-environmental-exposures-early.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.