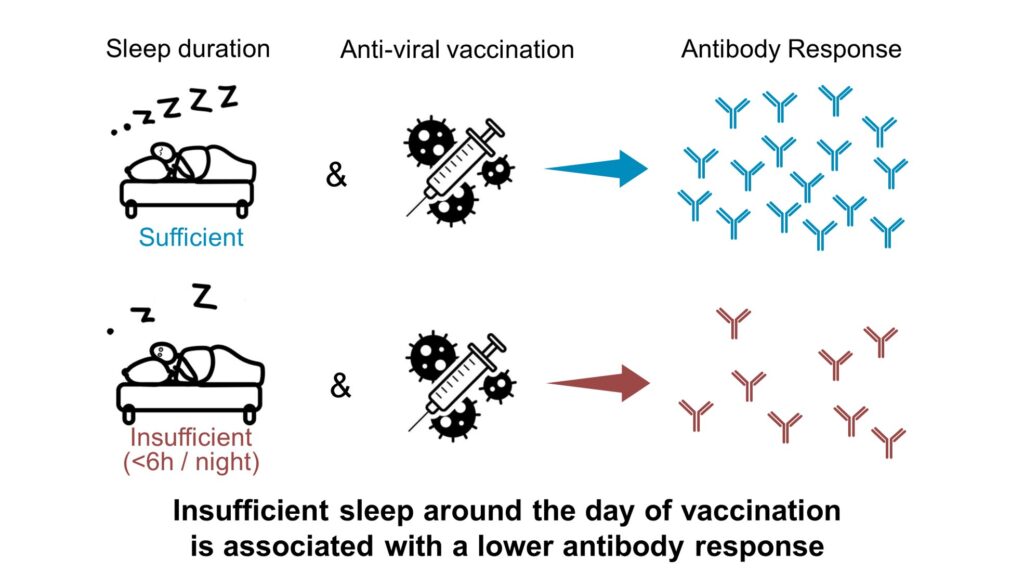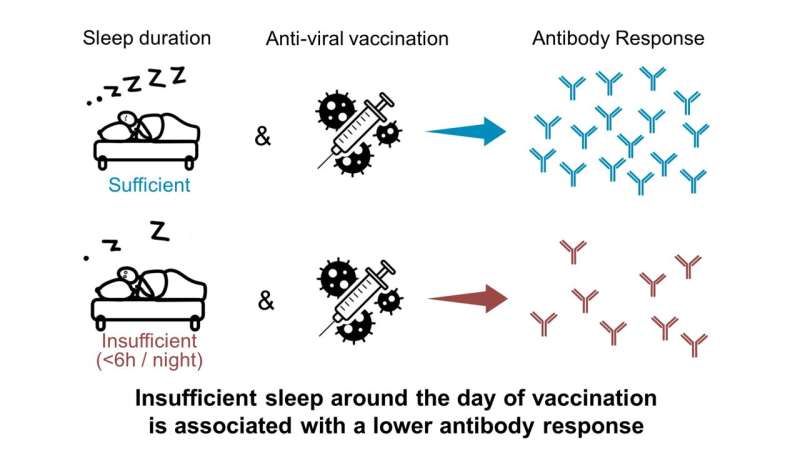
In reviewing knowledge from earlier research, a group lead by researchers on the College of Chicago and the French Nationwide Institute of Well being and Medical Analysis (Inserm) discovered that people who had fewer than six hours of sleep per night time within the days surrounding vaccination had a blunted antibody response. That signifies efforts to advertise heathy sleep period forward of an immunization could possibly be a simple means to enhance vaccine effectiveness. The research was printed March 13 in Present Biology.
The newest work builds on a 2002 research by members of the group displaying that proscribing sleep in contributors diminished their antibody response to influenza vaccination, resulting in about half of the antibody ranges seen in controls at 10 days after an inoculation. Their curiosity within the work was revived throughout the COVID-19 pandemic lockdowns in 2020, once they started to attach with others who had studied this query and began to drag collectively the meta-analysis.
Throughout seven research, which examined the influence of sleep period on vaccination towards viral diseases comparable to influenza and hepatitis, the researchers discovered that inadequate sleep (outlined as below six hours of sleep per night time) within the days surrounding vaccination resulted in a decreased antibody response.
“Inadequate sleep is a behavioral issue that may be corrected earlier than vaccination and will not solely strengthen, but additionally lengthen, the vaccine response,” mentioned Eve Van Cauter, Ph.D., Professor Emeritus of Drugs at UChicago and senior creator on the meta-analysis. “We all know that individuals reply otherwise to vaccination in response to their age, intercourse, present medical situations and different elements that can’t be readily modified. Having an simply modifiable habits that you would be able to modify across the time of your appointment provides you one thing you possibly can management that’s seemingly to enhance your physique’s response.”
Importantly, the affiliation was seen solely in research that objectively assessed sleep period utilizing wearable exercise trackers or sleep research within the laboratory. Self-reported sleep period was not a predictor of vaccine response. The researchers famous that whereas the affiliation was robust for males, it was weaker and never statistically important for ladies. They argue this was seemingly as a consequence of the truth that not one of the research in girls accounted for variations in intercourse hormone ranges by menstrual cycle, use of contraceptives and menopausal standing.
“The hyperlink between sleep and vaccine effectiveness could possibly be a serious concern for individuals with irregular work schedules, particularly for shift employees who usually have decreased sleep period,” mentioned Van Cauter. “That is one thing individuals ought to take into account planning round, to make sure that they’re getting sufficient sleep within the week earlier than and after their vaccines.”
Utilizing the outcomes of the meta-analysis and evaluating to recognized knowledge on the antibody response to the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, the researchers estimated that the results of inadequate sleep on the vaccine response could be equal to 2 months of waning antibodies after vaccination.
“Apparently, we noticed the identical outcomes in each influenza, which is a respiratory virus, and hepatitis, which impacts the liver, suggesting that this impact may lengthen to every kind of viruses, together with coronaviruses like SARS-CoV-2,” mentioned Karine Spiegel, Ph.D., first creator on the research and a analysis scientist at Inserm. “Total, we see these outcomes as a name to motion.”
The researchers hope that the research will encourage extra analysis into the phenomenon to make clear the results on women and men, in addition to to higher perceive how totally different vaccines could also be impacted by sleep period and the way sleep is perhaps optimized to advertise a greater vaccine response.
“We want a lot bigger research that management for the intercourse hormone surroundings in girls particularly,” mentioned Spiegel. “We additionally want a greater definition of what number of days of quick sleep period have an effect on the antibody response, and whether or not it’s simply earlier than the vaccine, or additionally throughout and after. Giant scale research that take into account behavioral, demographic and hormonal traits ought to present new insights that may translate to measurable impacts on vaccine efficacy.”
“The immune system will not be the one one modulated by sleep,” mentioned Van Cauter. “Inadequate sleep is linked to different well being points comparable to an elevated threat of growing weight problems, diabetes or hypertension. Vaccines are an essential instrument for stopping and lowering the impacts of infectious illnesses, and we expect that you just might be able to implement a easy behavioral change—getting sufficient sleep—to derive a direct profit. It is low-cost, and there’s no opposed impact.”
Extra data:
Karine Spiegel, A meta-analysis of the associations between inadequate sleep period and antibody response to vaccination, Present Biology (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2023.02.017. www.cell.com/current-biology/f … 0960-9822(23)00156-2
College of Chicago Medical Heart
Quotation:
Not getting sufficient sleep may blunt antibody response to vaccination, leaving you extra susceptible to an infection (2023, March 13)
retrieved 13 March 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-03-blunt-antibody-response-vaccination-vulnerable.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.