Beta blockers have lengthy been extensively prescribed for sufferers with coronary heart points, however two new research this week query the good thing about the therapies in sure sufferers with robust coronary heart perform.
One examine, printed Tuesday in Coronary heart, checked out individuals who skilled a coronary heart assault however didn’t develop coronary heart failure or dysfunction of their coronary heart’s pumping. Researchers discovered that long-term beta blocker use wasn’t related to improved cardiovascular outcomes on this group.
The opposite examine, printed Wednesday in JACC: Coronary heart Failure, targeted on individuals with coronary heart failure who had mildly lowered and regular ejection fraction, which is a measure of a coronary heart’s squeezing perform. The authors discovered that beta blockers had been linked to a better danger of hospitalization in sufferers with larger squeezing energy.
Beta blockers lead the guts to beat extra slowly and are supposed to decrease stress on the guts. Docs have been prescribing the drugs based mostly on information from many years in the past earlier than current developments in cardiovascular care, and sufferers additionally typically have comorbidities that lead docs to prescribe beta blockers. Whereas the 2 research are each observational, and the authors pressured the necessity for extra analysis that follows sufferers over time, the findings nonetheless counsel that the longstanding observe of prescribing beta blockers deserves reassessment.
The info are “all pointing to an identical route that not all sufferers that we used to traditionally reflexively placed on beta blockers profit from beta blockers,” stated Lakshmi Sridharan, a complicated coronary heart failure and transplant heart specialist at Emory College who wasn’t concerned within the research.
“Now could be the time to be personalised and individualized in our decision-making” on sufferers’ remedy plans, she stated.
The examine in Coronary heart analyzed well being data from over 43,000 adults in Sweden who skilled a coronary heart assault however didn’t have coronary heart failure or pumping dysfunction. Whereas there’s analysis supporting the usage of beta blockers shortly after a coronary heart assault in most of these sufferers, there’s little information longer-term use, so the researchers targeted on beta blocker utilization one yr after a coronary heart assault.
Of the sufferers studied, a majority of them — 79% — had been on beta blockers a yr after a coronary heart assault. After adjusting and weighting for elements comparable to demographics and comorbidities, the researchers discovered no distinction within the danger of demise and cardiovascular incidents between individuals who had been and weren’t on beta blockers throughout a median observe up of 4.5 years.
Gorav Batra, the senior creator and advisor heart specialist at Uppsala College in Sweden, stated the care and remedy of sufferers with coronary heart assaults has vastly improved during the last three many years. Which means sufferers expertise much less harm to their coronary heart muscle from coronary heart assaults, and they also might not want beta blockers long run to assist them.
Sridharan famous that for the reason that examine was carried out in Sweden, its findings is probably not generalizable to the U.S. inhabitants.
Nonetheless, she stated, it’s essential to look at the usage of beta blockers since coronary heart assault care has superior and for the reason that medication can include negative effects that have an effect on sufferers’ high quality of life, comparable to fatigue and despair. “That’s when the query of the risk-benefit ratio actually comes into play for these sufferers,” she stated.
The opposite examine printed in JACC: Coronary heart Failure checked out over 400,000 individuals within the U.S. over the age of 65 who had coronary heart failure with mildly lowered or regular squeezing perform, described as an ejection fraction better than 40%.
Whereas research have persistently proven the good thing about beta blockers in coronary heart failure sufferers with considerably lowered squeezing energy, measured as an ejection fraction lower than 40%, there’s restricted information on use of the medication in individuals with stronger squeezing perform.

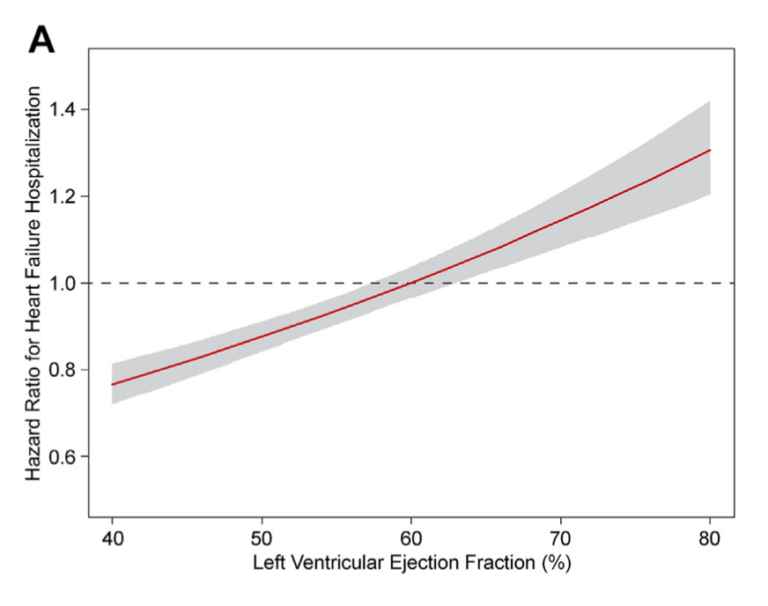
But once more right here, most sufferers studied — 66% — had been on beta blockers. After adjusting for elements like comorbidities and well being historical past, and in a median followup of 38 months, the researchers discovered that because the ejection fraction quantity elevated, the chance of hospitalization for coronary heart failure linked to beta blocker use additionally elevated.
Amongst sufferers with a mildly lowered ejection fraction, beta blockers had been related to a decrease danger of hospitalization and demise. However amongst sufferers with better squeezing perform, significantly these with an ejection fraction over 60%, beta blockers had been linked to larger hospitalization charges.
The researchers additionally discovered that this development held whether or not or not sufferers had hypertension, an irregular heartbeat, or coronary artery illness — that are three comorbidities that at the moment lead docs to prescribe beta blockers.
The examine suggests “you actually have to concentrate to what the ejection fraction is” when treating coronary heart failure sufferers, stated Suzanne Arnold, the lead creator and a professor of medication on the College of Missouri-Kansas Metropolis.
Michelle Kittleson, director of coronary heart failure analysis on the Smidt Coronary heart Institute at Cedars-Sinai, stated the research present the significance of reviewing the drugs every affected person is on and justifying their want.
Whereas beta blockers have been round for a very long time, there hasn’t been a lot analysis probing their utility for varied affected person teams.
“That’s inertia in medication — it’s very laborious to cease a medication, it’s very laborious to say no, it’s very laborious to backtrack,” Kittleson stated. “It takes numerous activation power to do a deep dive and determine if one thing is required.”
STAT’s protection of continual well being points is supported by a grant from Bloomberg Philanthropies. Our monetary supporters usually are not concerned in any choices about our journalism.