Daytime napping could assist to protect mind well being by slowing the speed at which our brains shrink as we age, suggests a brand new research led by researchers at UCL and the College of the Republic in Uruguay.
The research, printed within the journal Sleep Well being, analyzed information from individuals aged 40 to 69 and located a causal hyperlink between routine napping and bigger whole mind quantity—a marker of excellent mind well being linked to a decrease danger of dementia and different illnesses.
Senior creator Dr. Victoria Garfield (MRC Unit for Lifelong Well being & Ageing at UCL) mentioned, “Our findings recommend that, for some individuals, brief daytime naps could also be part of the puzzle that would assist protect the well being of the mind as we grow old.”
Earlier analysis has proven that napping has cognitive advantages, with individuals who have had a brief nap performing higher in cognitive checks within the hours afterwards than counterparts who didn’t nap.
The brand new research aimed to ascertain if there was a causal relationship between daytime napping and mind well being.
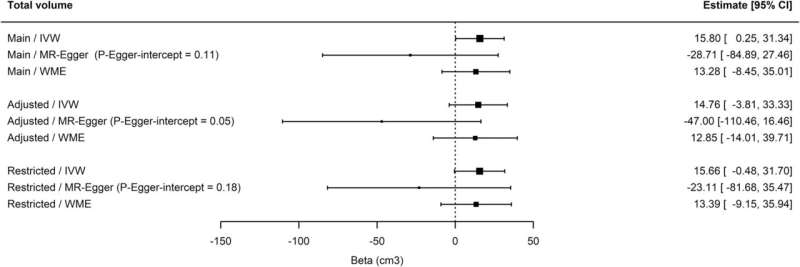
Utilizing a method referred to as Mendelian randomization, they checked out 97 snippets of DNA thought to find out individuals’s chance of routine napping. They in contrast measures of mind well being and cognition of people who find themselves extra genetically “programmed” to nap with counterparts who didn’t have these genetic variants, utilizing information from 378,932 individuals from the UK Biobank research, and located that, general, individuals predetermined to nap had a bigger whole mind quantity.
The analysis group estimated that the typical distinction in mind quantity between individuals programmed to be routine nappers and those that weren’t was equal to 2.6 to six.5 years of growing older.
However the researchers didn’t discover a distinction in how effectively these programmed to be routine nappers carried out on three different measures of mind well being and cognitive perform—hippocampal quantity, response time and visible processing.
Lead creator and Ph.D. candidate Valentina Paz (College of the Republic (Uruguay) and MRC Unit for Lifelong Well being & Ageing at UCL) mentioned, “That is the primary research to aim to untangle the causal relationship between routine daytime napping and cognitive and structural mind outcomes. By taking a look at genes set at delivery, Mendelian randomization avoids confounding components occurring all through life which will affect associations between napping and well being outcomes. Our research factors to a causal hyperlink between routine napping and bigger whole mind quantity.”
Dr. Garfield added, “I hope research resembling this one displaying the well being advantages of brief naps can assist to scale back any stigma that also exists round daytime napping.”
The genetic variants influencing our chance to nap had been recognized in an earlier research taking a look at information from 452,633 UK Biobank members. The research, led by Dr. Hassan Dashti (Harvard College and Massachusetts Common Hospital), additionally an creator on the brand new research, recognized the variants on the idea of self-reported napping, and this was supported by goal measurements of bodily exercise recorded by a wrist-worn accelerometer.
Within the new research, researchers analyzed well being and cognition outcomes for individuals with these genetic variants in addition to a number of totally different subsets of those variants, adjusted to keep away from potential bias, as an example avoiding variants linked to extreme daytime sleepiness.
Genetic information and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of the mind had been accessible for 35,080 people drawn from the bigger UK Biobank pattern.
When it comes to research limitations, the authors famous that all the members had been of white European ancestry, so the findings won’t be instantly generalizable to different ethnicities.
Whereas the researchers didn’t have info on nap period, earlier research recommend that naps of half-hour or much less present one of the best short-term cognitive advantages, and napping earlier within the day is much less more likely to disrupt night-time sleep.
Extra info:
Valentina Paz et al, Is there an affiliation between daytime napping, cognitive perform, and mind quantity? A Mendelian randomization research within the UK Biobank, Sleep Well being (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.sleh.2023.05.002
College School London
Quotation:
Common napping linked to bigger mind quantity (2023, June 20)
retrieved 20 June 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-06-regular-napping-linked-larger-brain.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.


