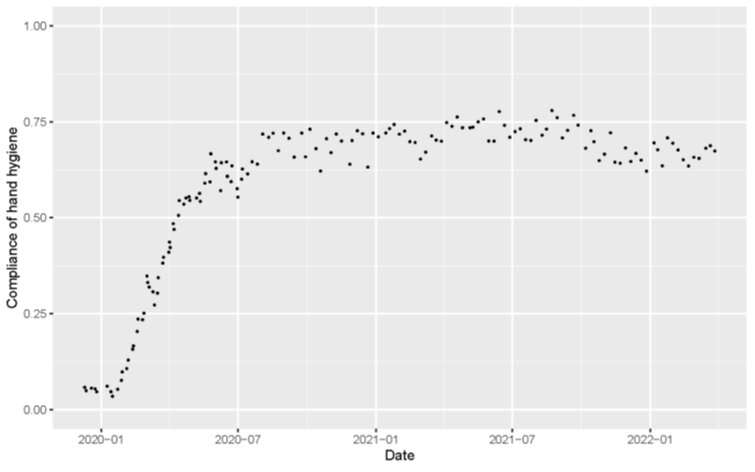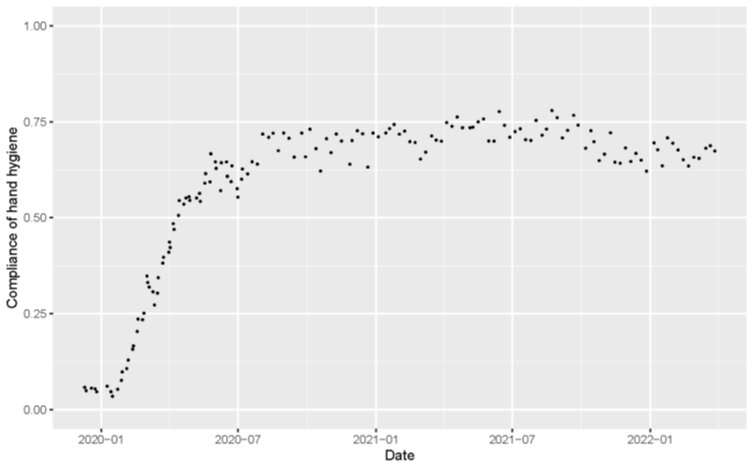
Lengthy earlier than COVID-19, washing and sterilizing arms had been recognized to assist forestall the unfold of infections similar to influenza, and hand hygiene practices had been particularly essential in high-risk areas, similar to hospitals. So it was one thing of a public well being boon that COVID-19 abruptly elevated hand hygiene consciousness. A brand new research additionally discovered that media protection of the pandemic had a knock-on impact.
The research, from Japan’s Osaka College, gained distinctive perception on how COVID-19’s onset and media protection of the novel virus raised hand hygiene compliance from 5% to over 70% in a matter of months. The research’s researchers tracked whether or not TV protection associated to such compliance and sought correlations between hand hygiene and newly confirmed COVID-19 instances and deaths. Their article, “The influence of tv on-air time readily available hygiene compliance behaviors throughout COVID-19 outbreak,” was revealed within the American Journal of An infection Management.
“We had been routinely monitoring hospital guests’ use of hand sterilizer in December 2019 due to the influenza season,” explains lead creator Daiichi Morii. “The timing simply occurred to correspond with the pandemic onset. That permit us evaluate hand hygiene compliance earlier than, throughout, and after the onset.” As one other analysis variable, TV protection was used as an emblem of the diploma of social concern about COVID-19, and checked out its correlation with compliance.
Guests had been noticed to see whether or not they voluntarily used alcohol spray on their arms upon coming into hospital premises. Throughout the baseline statement interval in December 2019, simply 5.3% of the noticed guests sanitized their arms. On January 28, 2020, the quantity rose modestly to 7.6%. Then, as COVID-19 rapidly emerged, issues took a dramatic shift—compliance rose to close 70% by August 2020 and remained at 70%–75% till October 2021, earlier than very step by step declining.
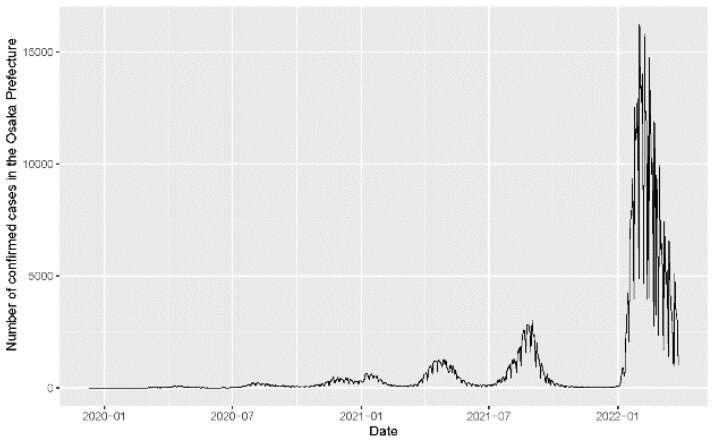
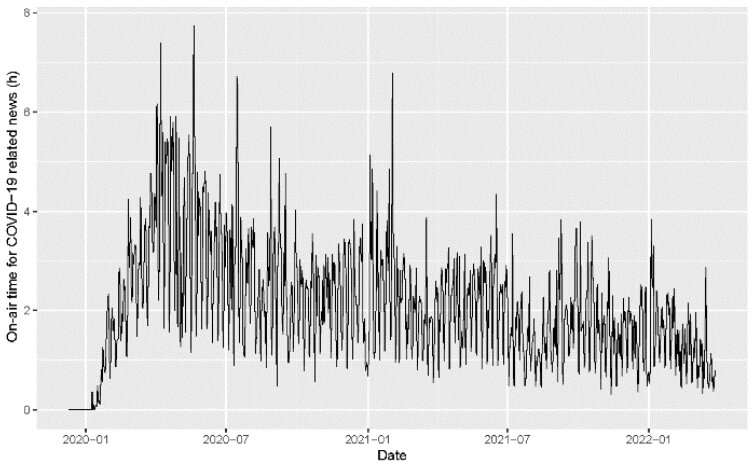
On the identical time, the researchers needed to look at how the extent of societal concern affected hand hygiene compliance. “Media protection can have a robust psychological influence and have an effect on public concern,” notes co-author Asako Miura. “So we checked out on-air time overlaying COVID-19 on Japan’s nationwide public TV broadcaster, NHK, within the area the place the hospital is situated. The time spiked at 7.7 hours/day in Might 2020, after which different relying on the an infection development.”
The researchers ran mathematical simulations to pair TV protection with compliance, and located a robust statistical correlation—an added hour of stories protection elevated compliance the following day by round 1%. Additionally they tracked the traits in newly confirmed COVID-19 instances and deaths, however discovered no correlation with hand hygiene compliance.
Regardless of the massive improve in hand hygiene compliance when there’s an epidemic onset, and the evident position media performs in that compliance, complacency can set in. Folks hear the identical warnings time and again, because the authors be aware, and develop bored with them. Extra analysis is due to this fact wanted into find out how to keep the constructive impacts seen on this research. That upkeep might result in a future with much less infectious illness, and clear arms.
Extra info:
Daiichi MORII et al, The influence of tv on-air time readily available hygiene compliance behaviors throughout COVID-19 outbreak, American Journal of An infection Management (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.ajic.2023.03.001
Osaka College
Quotation:
Tune in, wash arms: Examine finds COVID-19 TV protection added momentum at hand hygiene increase (2023, March 15)
retrieved 16 March 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-03-tune-covid-tv-coverage-added.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.