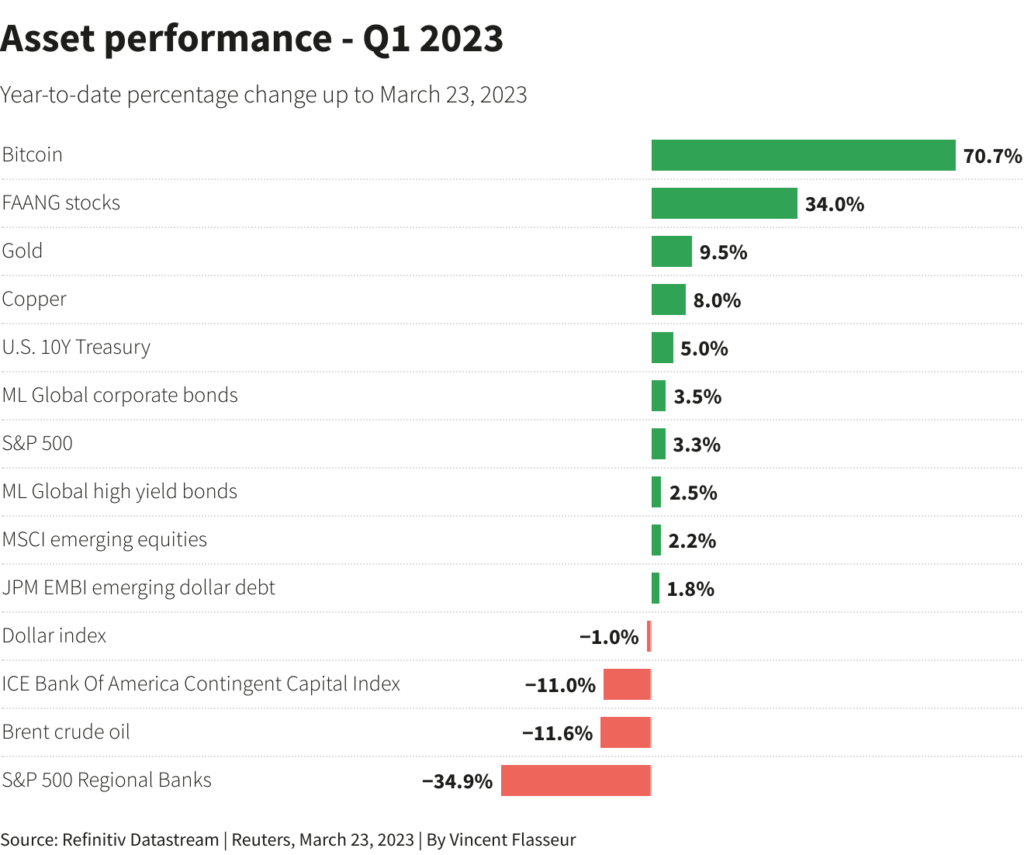
LONDON, March 27 (Reuters) – At an unimaginable finish to the primary quarter for monetary markets, rattled by financial institution turmoil, some stability shall be a lot hoped for in coming days.
However do not wager on it. Regional U.S. banking shares stay close to their lowest ranges in two years, Europe is weighing up the fallout from the pressured UBS-Credit score Suisse tie-up. And knowledge will present how a lot the market ructions are making recession extra seemingly.
This is a have a look at the week forward in markets from Kevin Buckland in Tokyo, Lewis Krauskopf in New York and Naomi Rovnick, Amanda Cooper and Dhara Ranasinghe in London.
1/ A COCO-NUTS QUARTER
What 1 / 4. January noticed the most important rush into equities for the primary month of the yr on file as buyers loaded up on low cost shares. With “peak charges” primarily priced in, bond yields at multi-year highs out of the blue seemed juicy. The specter of inflation seemed much less extreme and development extra strong. Disaster averted!
Quick-forward just a few weeks and a slew of crypto-companies have folded, U.S. regional banks shares have tanked within the wake of Silicon Valley Financial institution collapse and 167-year outdated Credit score Suisse has imploded – and the writedown of a few of its contingent convertible bonds (CoCos) has whipped market volatility right into a 2008-style frenzy.
“Peak charges” is coming sooner than many anticipated, not as a result of inflation has been vanquished, however as a result of central banks are cautious of fanning the flames of a credit score crunch, proper because the banking sector wobbles.
2/ DON’T BANK ON IT
The collapse of Silicon Valley Financial institution, a 90% share worth drop over two weeks in beleaguered First Republic Financial institution (FRC.N) and a shotgun marriage between Credit score Suisse (CSGN.S) and UBS (UBSG.S) to avert a wider disaster: banks have gone on a wild trip.
The turmoil will not be over but. Shares of Germany’s largest financial institution Deutsche Financial institution plunged on Friday whereas wider indicators of monetary market stress have been additionally flashing.
SNB chief Thomas Jordan reckons the subsequent two weeks shall be important to securing UBS’s Credit score Suisse takeover. Fed Chair Jerome Powell mentioned banking stress might set off a credit score crunch with “vital” implications for a slowing U.S. economic system.
And at the same time as central banks and governments step in to stem indicators of panic, there is a new problem to grapple with – a social media-driven financial institution run that may be onerous to manage as soon as hearsay and concern take maintain.
As Citigroup (C.N) chief govt Jane Fraser places it, social media is a “full game-changer” in financial institution runs.
In the meantime, Swiss monetary regulator FINMA mentioned it was contemplating whether or not to take disciplinary motion towards Credit score Suisse managers.
3/ DID YOU SAY AT1?
Credit score Suisse’s pressured takeover by UBS concerned $17 billion of Further Tier 1 debt, shock absorbers if a financial institution’s capital ranges fall beneath a threshold, being worn out.
Costs of banks’ AT1s bonds tumbled following the information. Hong Kong, Singapore, the European Union and Britain stepped into to calm the unease.
Potential authorized motion can be doable after Swiss authorities dominated that holders of Credit score Suisse AT1 bonds would get nothing within the deal. Shareholders, who often rank beneath debt buyers when an organization turns into bancrupt, will obtain $3.23 billion.
Attorneys are assessing whether or not there’s a case towards the Swiss authorities. How this performs out in coming days shall be watched intently.
The saga has additionally rocked the $275 billion AT1 bond market, as buyers scrutinise debt prospectuses for clauses that would solid doubt over restoration prospects.
4/ DATA DIVE
U.S. knowledge that may give perception into the well being of the buyer and the state of inflation is well timed for buyers making an attempt to weigh up whether or not the economic system can stave off a downturn.
The banking disaster has prompted fears that lending will sluggish, grinding the gears of the economic system.
March’s studying of shopper confidence is due on Tuesday. The index unexpectedly fell in February.
On Friday, the February private consumption expenditure index will provide one other have a look at inflation. It accelerated in January, feeding fears a few extra hawkish Federal Reserve.
The Fed raised charges by one other quarter level on Wednesday, however recast its outlook from a hawkish preoccupation with inflation to a extra cautious stance, given market turmoil that has tightened monetary circumstances.
5/ INFLATION WATCH
Incoming Financial institution of Japan Governor Kazuo Ueda shall be watching newest Tokyo inflation knowledge intently.
In spite of everything, Ueda has the load of his predecessor’s decade of large stimulus on his shoulders when he takes over in April.
Expectations are excessive that he’ll mastermind a fragile unwinding of yield curve controls and adverse rates of interest throughout his tenure, however a key query is when.
Ueda is in no rush, however strain is constructing.
The discharge of Tokyo CPI for March on March 31 is prone to present inflation has topped the BOJ’s 2% goal for a tenth straight month. And wage inflation exhibits indicators of catching up.
However policymakers say the financial restoration stays fragile. And U.S. and European banks turmoil present how shortly a disaster can floor, giving Ueda much more purpose for warning.
Graphics by Prinz Magtulis, Vincent Flasseur, Riddhima Talwani; Compiled by Dhara Ranasinghe; Modifying by Bradley Perrett
: .