A bunch of scientists say they’ve discovered new proof to again up their principle that advanced life on Earth might have begun 1.5bn years sooner than thought.
The staff, working in Gabon, say they found proof deep inside rocks displaying environmental circumstances for animal life 2.1bn years in the past.
However they are saying the organisms have been restricted to an inland sea, didn’t unfold globally and ultimately died out.
The concepts are an enormous departure from typical considering and never all scientists agree.
Most consultants consider animal life started round 635m years in the past.
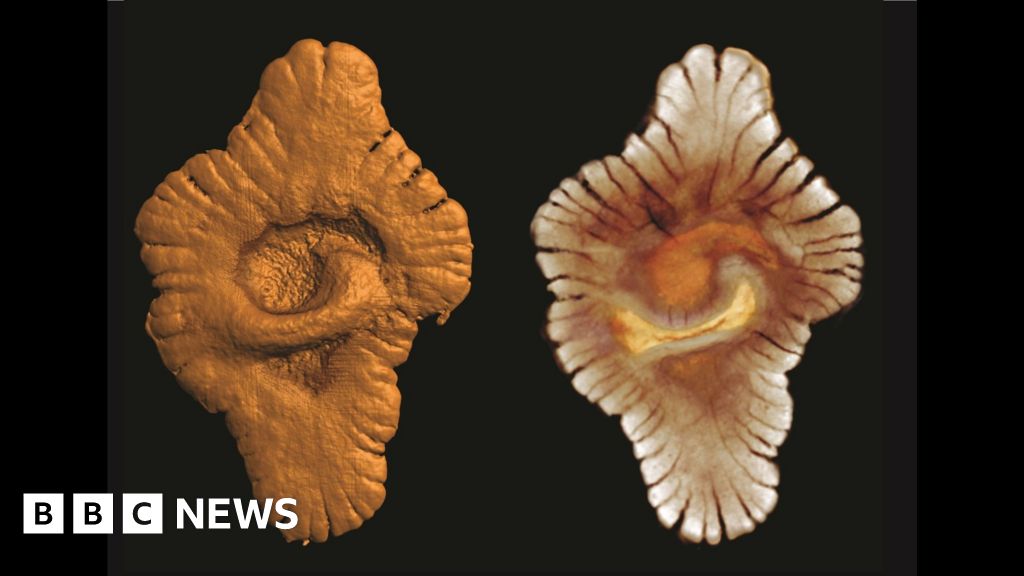
The analysis provides to an ongoing debate over whether or not so-far unexplained formations present in Franceville, Gabon are literally fossils or not.
The scientists appeared on the rock across the formations to see in the event that they confirmed proof of containing vitamins like oxygen and phosphorus that might have supported life.
Professor Ernest Chi Fru at Cardiff College labored with a world staff of scientists.
He instructed BBC Information that, if his principle is appropriate, these life kinds would have been much like slime mould – a brainless single-cell organism that reproduces with spores.
However Professor Graham Shields at College Faculty London, who was not concerned within the analysis, says he had some reservations.
“I am not in opposition to the concept that there have been greater vitamins 2.1bn years in the past however I am not satisfied that this might result in diversification to type advanced life,” he mentioned, suggesting extra proof was wanted.
Prof Chi Fru mentioned his work helped show concepts concerning the processes that create life on Earth.
“We’re saying, look, there’s fossils right here, there’s oxygen, it is stimulated the looks of the primary advanced residing organisms,” he mentioned.
“We see the identical course of as within the Cambrian interval, 635m years in the past – it helps again that up. It helps us perceive finally the place we’ve got all come from,” he added.
The primary trace that advanced life may have begun sooner than beforehand thought took place 10 years in the past with the invention of one thing known as the Francevillian formation.
Prof Chi Fru and his colleagues mentioned the formation was made up of fossils which pointed to proof of life that might “wiggle” and transfer of its personal accord.
The findings weren’t accepted by all scientists.
To seek out extra proof for his or her theories, Prof Chi Fru and his staff have now analysed sediment cores drilled from the rock in Gabon.
The chemistry of the rock confirmed proof {that a} “laboratory” for all times was created simply earlier than the formation appeared.
They consider that the excessive ranges of oxygen and phosphorus have been made by two continental plates colliding below water, creating volcanic exercise.
The collision minimize off a bit of water from the oceans, making a “nutrient-rich shallow marine inland sea.”
Prof Chi Fru says this protected atmosphere had the circumstances to permit photosynthesis, resulting in vital quantities of oxygen within the water.
“This could have supplied enough vitality to advertise will increase in physique measurement and larger advanced behaviour noticed in primitive, easy animal-like life kinds akin to these discovered within the fossils from this era,” he mentioned.
However he says that the remoted atmosphere additionally led to the demise of the life kinds as a result of there weren’t sufficient new vitamins fed in to maintain a meals provide.
PhD scholar Elias Rugen on the Pure Historical past Museum, who was not concerned within the analysis, agreed with a few of the findings, saying it is clear that “oceanic carbon, nitrogen, iron and phosphorus cycles have been all doing one thing just a little bit unprecedented at this level in Earth’s historical past.”
“There’s nothing to say that advanced organic life couldn’t have emerged and thrived way back to 2bn years in the past,” he mentioned, however added that extra proof was wanted to assist the theories.
The findings are revealed in the scientific journal Precambrian Analysis.