
Greater than three years into the COVID pandemic, each the virus and the measures taken to manage its unfold have affected individuals’s lives throughout the globe. However how can we totally quantify these results?
Whereas we’ve got estimates of how many individuals have died from COVID globally (which at present run at just below 7 million), its broader results—together with psychological well being deterioration due, for instance, to the anxiousness of getting contaminated or the isolation of lockdowns—have obtained much less analysis consideration.
In a brand new research printed in PLOS Medication, we have tried to quantify how the COVID pandemic has affected world well being utilizing a world survey of most people.
Well being economists usually quantify well being utilizing a metric referred to as the quality-adjusted life yr (QALY). The thought is to assign a price to every yr of an individual’s life based mostly on their total well being. An individual in full well being will get a rating of 1 and those that are very ailing near zero.
A standard method to measure QALYs is thru a quick survey known as the EQ-5D, which includes 5 questions masking key dimensions of well being. An individual charges their ranges of mobility, self care, traditional actions, ache and discomfort, and anxiousness and despair.
The responses present a profile of the individual’s health-related high quality of life, which is summarized by what’s referred to as the EQ-5D index. When measured at completely different closing dates this can be utilized to estimate QALYs, which regulate life expectancy to take account of total well being.
For instance, an individual in comparatively poor well being might have an EQ-5D index of 0.5 and they also would accumulate one QALY for each two years they reside. This system has been broadly used to guage the impacts of various ailments and coverings on well being.
We measured total health-related high quality of life by together with the EQ-5D in a worldwide survey of the general public in late 2020, on the finish of the primary yr of the pandemic, simply earlier than COVID vaccines began to be distributed. The survey was performed on-line on simply over 15,000 individuals in 13 numerous nations.
To establish how individuals thought the pandemic had affected them, we requested them to charge their present well being in contrast with a yr earlier than.
One limitation of our research is that we needed to depend on individuals with the ability to recall what their well being was like previous to the pandemic. Whereas it is unlikely that an individual is ready to recall precisely how they’d have responded to the survey a yr prior to now, there may be proof that over and under-estimation errors are likely to cancel one another out.
What we discovered
The pandemic was related to considerably worse health-related high quality of life for greater than one-third of respondents. Nervousness and despair was the side of well being that worsened essentially the most, particularly for youthful individuals (aged underneath 35) and girls.
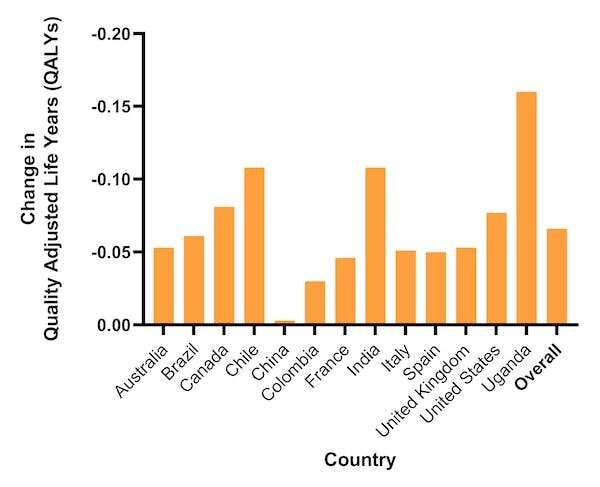
Translating the well being reductions right into a QALY measure indicated that throughout the pandemic perceived well being was round 8% decrease on common.
Trying on the outcomes by nation, these most affected had been center revenue nations together with India (which had lockdowns for over 40 weeks) and Chile (which had a excessive charge of COVID infections).
In distinction, members in China notably reported no vital deterioration of their well being standing. Though there have been lockdowns in China following the emergence of the virus in early 2020, low ranges of transmission meant that these had been eliminated inside a couple of weeks.
To place the outcomes into context, earlier research have discovered that every COVID loss of life leads to the lack of a median of between three and 6 QALYs. We mixed these estimates with the reported variety of deaths in every nation to quantify the influence of COVID deaths on total QALYs in every nation.
Primarily based on the reported modifications in well being in our survey, the loss in QALYs as a result of COVID pandemic and lockdowns was between 5 and 11 occasions bigger than that resulting from COVID-related deaths. This highlights that solely specializing in COVID circumstances and deaths overlooks the burden of the pandemic and the impacts of insurance policies which might be designed to manage it.
For instance, most nations used some type of lockdowns as a method to comprise transmission of the virus, however the ensuing social isolation might have negatively affected the psychological well being and well-being of the inhabitants. Equally, some nations provided financial assist to these in monetary difficulties, which can have positively impacted their psychological well-being. QALYs present a means of quantifying the trade-offs that exist between the optimistic and damaging results of various methods.
Classes for future pandemics
Whereas particular person nations have sought to measure the pandemic’s results on total well-being, the restricted variety of worldwide research particular facets of well being, reminiscent of psychological well being, have tended to give attention to excessive revenue nations. Most world analyses of the results of the pandemic depend on reported COVID circumstances and associated deaths.
The common measurement of various facets of well being in a standardized survey permits researchers to begin to disentangle the results of lockdowns and different insurance policies from the impacts of COVID.
Measuring a number of facets of well being via QALYs would even be a helpful complement to current measures specializing in circumstances and deaths. This could allow us to take a look at a number of the results of the COVID pandemic as they’re distributed throughout the inhabitants. For instance, whereas deaths are highest in older individuals, psychological well being results had been extra outstanding in these underneath 35.
Shifting past counting deaths to understanding the general well being of the inhabitants globally might help us to be higher ready for potential future well being shocks.
Extra info:
Mara Violato et al, The COVID-19 pandemic and health-related high quality of life throughout 13 high- and low-middle-income nations: A cross-sectional evaluation, PLOS Medication (2023). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004146
The Dialog
This text is republished from The Dialog underneath a Inventive Commons license. Learn the unique article.![]()
Quotation:
Why specializing in COVID deaths undercounts the well being harms of the pandemic: New analysis (2023, April 13)
retrieved 14 April 2023
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2023-04-focusing-covid-deaths-undercounts-health.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.


