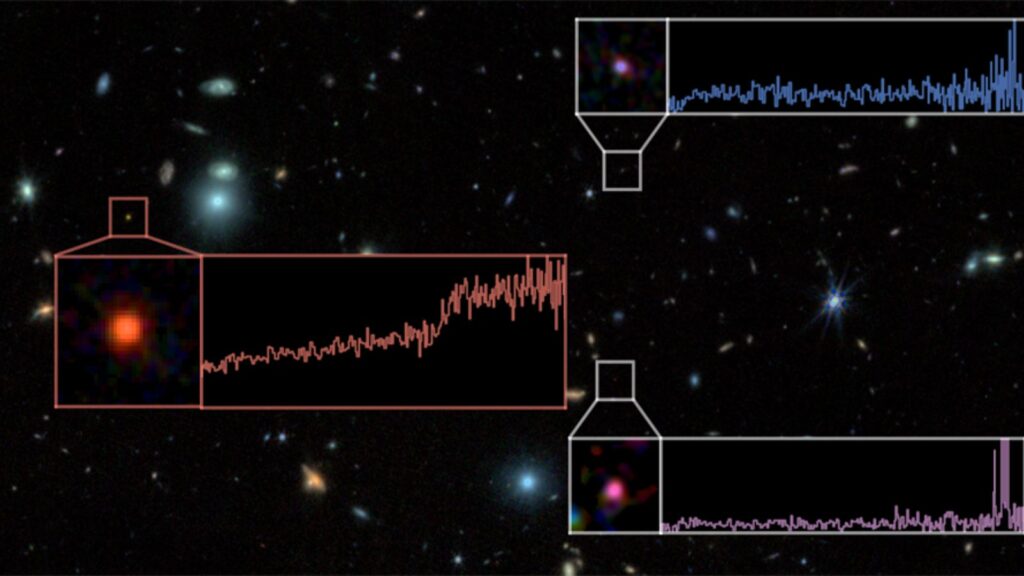
Greater than 13 billion years after the Huge Bang, astronomers have discovered essentially the most distant galaxy ever seen utilizing the James Webb Area Telescope (JSWT), besides that this one has already stopped forming stars.
The JWST noticed gentle from this newly found ‘useless galaxy’ referred to as RUBIES-UDS-QG-z7,(the Pink Unknowns: Vivid Infrared Extragalactic Survey). It’s stated to be essentially the most distant and big ‘useless galaxy’ to have been discovered until date.
The invention was made by a global group, led by astronomers from the College of Geneva (UNIGE) in Geneva, Switzerland. “For a very long time, scientists thought that solely actively star-forming galaxies ought to be noticed within the very early Universe. The James Webb area telescope now reveals that galaxies stopped forming stars sooner than anticipated,” in response to a press launch issued by the College on April 2, 2025.
So, what’s a useless galaxy? What results in their formation? What’s galaxy quenching? Why does the latest discovery matter?
What’s a useless galaxy?
A galaxy that has stopped creating new stars is known as a “useless galaxy”. This occurs when a galaxy makes use of up its provide of fuel, primarily hydrogen, which is important for the delivery of latest stars. With out sufficient chilly and dense fuel, star formation turns into stagnant.
Processes like stellar winds, supernovae, or black gap exercise may expel this fuel. Because of this, the galaxy slowly fades, full of growing old stars and no new ones to switch them.
The oldest recognized “useless” galaxy, JADES-GS-z7-01-QU, was noticed by the James Webb Area Telescope (JWST) in March final 12 months. It stopped producing stars when the universe was simply 700 million years outdated.
Story continues beneath this advert
How do galaxies develop and die?
Galaxies develop by absorbing fuel and changing it into new stars. A galaxy could possibly draw fuel extra successfully as its mass grows, which hastens the formation of latest stars as this progress is without end. Galaxies finally undergo a course of often known as “quenching,” during which they cease forming stars and, in impact, cease rising.
What’s quenching?
The largest galaxies, which incessantly have an elliptical form, are significantly susceptible to quenching. Earlier than star formation stops, these galaxies sometimes take an extended interval to kind by increase massive stellar populations. Probably the most vital unsolved issues in astrophysics is what precisely causes galaxies to quench.
“Discovering the primary large galaxies that stopped making stars within the early universe is essential as a result of it helps us learn the way they have been fashioned.” in response to a analysis paper revealed by College of Geneva. “Scientists discovered one such galaxy that made stars equal to fifteen billion instances the mass of the Solar, however stopped creating new stars,” it added.
What subsequent?
At a distance of about 650 light-years, RUBIES-UDS-QG-z7’s small bodily measurement signifies a excessive stellar mass density that’s equal to the utmost central densities present in quiescent galaxies at barely decrease redshifts (z ~2–5). It’s potential that these galaxies will develop into the cores of the native universe’s oldest and most large elliptical galaxies.
Story continues beneath this advert
The Atacama Giant Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), Earth’s largest radio telescope mission, which has 66 antennas located within the Atacama Desert area of Northern Chile, could possibly help the JWST in its analysis of RUBIES-UDS-QG-z7.
“The invention of RUBIES-UDS-QG-z7 supplies the primary robust proof that the centres of some close by large ellipticals might have already been in place because the first few hundred million years of the Universe,” the analysis paper learn.
(This text has been curated by Disha Gupta, who’s an intern with the Indian Specific)